📘 Q4 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
SysOps 관리자가 AWS 계정에서 CloudTrail을 활성화했다.
만약 CloudTrail이 꺼지면 즉시 다시 켜져야 한다.
→ 코드를 따로 작성하지 않고 이 요구사항을 만족하려면?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. AWS Organizations
→ 여러 계정 관리용 서비스. CloudTrail 자동 복구와는 관계 없음 ❌ - B. AWS Config 규칙 (CloudTrail 구성 변경 감지 + 자동 수정)
→ CloudTrail이 꺼지면 AWS Config가 감지 → 자동으로 다시 켜줌 ✅ - C. AWS Config + Lambda
→ 가능은 하지만 Lambda 코드를 직접 작성해야 함. 문제에서 "사용자 정의 코드 없이"라고 했으므로 ❌ - D. EventBridge 스케줄링
→ 단순히 주기적으로 실행할 뿐, 실시간 복구 보장은 안 됨 ❌
✅ 정답: B
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudTrail = 누가, 언제, 어떤 API를 호출했는지 기록
- 문제 요구사항 = CloudTrail이 꺼져도 자동으로 다시 켜져야 함
- 해결 방법 = AWS Config 자동 수정(Auto Remediation)
- "CloudTrailLoggingEnabled" 규칙 사용
- **자동 수정(Auto remediation)**으로 AWS-ConfigureCloudTrailLogging 실행
즉, CloudTrail이 꺼지면 AWS Config가 바로 감지하고 자동으로 켜주는 역할을 합니다.
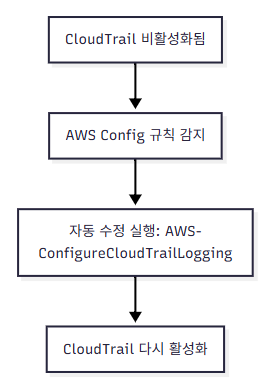
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[CloudTrail 비활성화됨] --> B[AWS Config 규칙 감지]
B --> C[자동 수정 실행: AWS-ConfigureCloudTrailLogging]
C --> D[CloudTrail 다시 활성화]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 CloudTrail 유지 = AWS Config + Auto Remediation
- "Config가 감시하고, 자동으로 켜준다" 라고만 기억하면 OK!
Q4.
A SysOps administrator has enabled AWS CloudTrail in an AWS account.
If CloudTrail is disabled, it must be re-enabled immediately.
What should the SysOps administrator do to meet these requirements WITHOUT writing custom code?
A. Add the AWS account to AWS Organizations.
Enable CloudTrail in the management account.
B. Create an AWS Config rule that is invoked when CloudTrail configuration changes.
Apply the AWS-ConfigureCloudTrailLogging automatic remediation action.
C. Create an AWS Config rule that is invoked when CloudTrail configuration changes.
Configure the rule to invoke an AWS Lambda function to enable CloudTrail.
D. Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Event) hourly rule with a schedule pattern to run an AWS Systems Manager Automation document to enable CloudTrail.
Answer: B
📘 Q5 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 ALB(Application Load Balancer) 뒤의 EC2 인스턴스에서 웹사이트를 운영 중
- DNS 관리는 Amazon Route 53에서 함
- 도메인의 zone apex (example.com)를 웹사이트와 연결하려고 함
👉 이때 어떤 DNS 레코드 타입을 사용해야 할까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. AAAA 레코드 (IPv6 주소 매핑)
→ zone apex 자체를 ALB에 바로 연결 불가 ❌ - B. A 레코드 (IPv4 주소 매핑)
→ ALB는 고정 IP가 없음. 따라서 직접 매핑 불가 ❌ - C. CNAME 레코드
→ zone apex에서는 CNAME 사용이 불가능 ❌ (RFC 표준 제약) - D. Alias 레코드
→ Route 53이 제공하는 특수 레코드
→ ALB, CloudFront, S3 등 AWS 리소스와 직접 연결 가능 ✅
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- ALB는 IP 주소가 변할 수 있어서 A/AAAA 레코드에 직접 연결할 수 없음.
- CNAME은 www.example.com 같은 서브도메인에서는 가능하지만, zone apex(example.com)에는 불가.
- AWS Route 53의 Alias 레코드는 이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 제공됨.
- 마치 CNAME처럼 동작하지만 zone apex에서도 사용 가능
- 추가 비용 없음
📊 Mermaid 시각화
U[사용자 브라우저] --> R53[Route 53]
R53 --> A[Alias Record]
A --> ALB[Application Load Balancer]
ALB --> EC2[웹 서버 EC2 인스턴스]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “zone apex = Alias 레코드”
- ALB, CloudFront, S3 정적 웹사이트를 example.com에 연결할 땐 항상 Alias!
Q5.
A company hosts its website on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer.
The company manages its DNS with Amazon Route 53, and wants to point its domain's zone apex to the website. Which type of record should be used to meet these requirements?
A. An AAAA record for the domain's zone apex
B. An A record for the domain's zone apex
C. A CNAME record for the domain's zone apex
D. An alias record for the domain's zone apex
Answer: D
📘 Q6 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 S3 버킷에 업로드되는 모든 객체가 반드시 암호화되었는지 확인해야 함
- 이 요구사항을 만족하는 방법 2가지 선택
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. AWS Shield 적용
→ DDoS 방어 서비스. 객체 암호화와는 관계 없음 ❌ - B. 객체 ACL로 제어
→ ACL은 접근 권한만 제어. 암호화 강제 불가 ❌ - C. S3 기본 암호화(Default Encryption)
→ 업로드 시 자동으로 암호화 처리 ✅ - D. Amazon Inspector 적용
→ 취약점 분석 툴. S3 암호화 확인 불가 ❌ - E. S3 버킷 정책으로 비암호화 객체 거부
→ "암호화 헤더 없는 업로드는 Deny" 정책 가능 ✅
✅ 정답: C, E
📝 쉬운 해설
- S3 기본 암호화(Default Encryption)
- 모든 업로드 객체를 자동으로 암호화
- 사용자가 별도 지정하지 않아도 안전하게 저장됨
- S3 버킷 정책(Bucket Policy)
- 업로드 요청에 x-amz-server-side-encryption 헤더가 없으면 거부(Deny)
- 암호화 강제 적용 가능
💡 두 방법을 함께 쓰면 자동 암호화 + 정책적 강제성으로 이중 보호!
📊 Mermaid 시각화
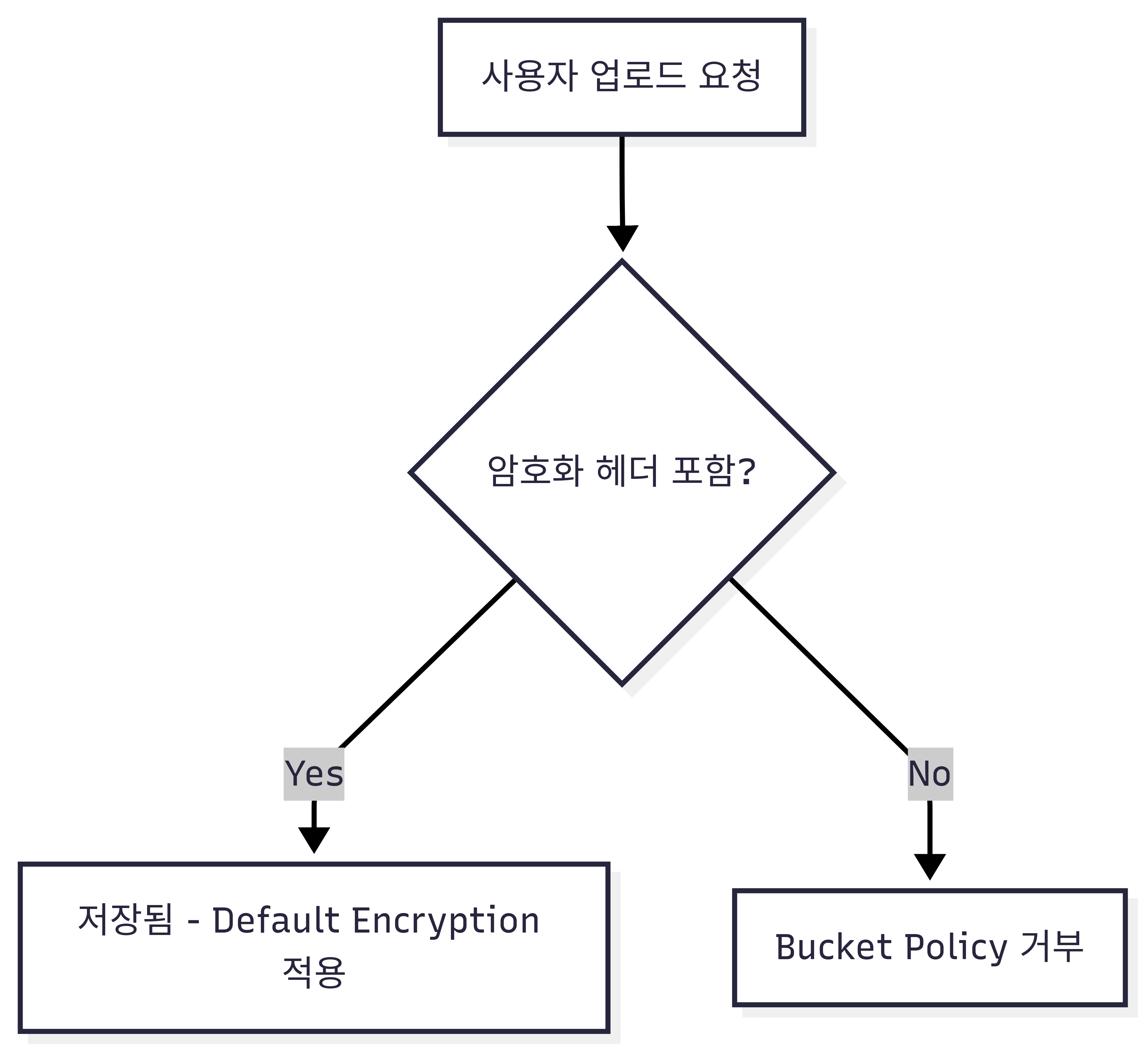
A[사용자 업로드 요청] --> B{암호화 헤더 포함?}
B -->|Yes| C[저장됨 (Default Encryption 적용)]
B -->|No| D[Bucket Policy 거부]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 "S3 암호화 = Default Encryption + Bucket Policy"
- Default Encryption = 자동 암호화
- Bucket Policy = 암호화 안 된 업로드 차단
Q6.
A company must ensure that any objects uploaded to an S3 bucket are encrypted.
Which of the following actions will meet this requirement? (Choose two)
A. Implement AWS Shield to protect against unencrypted objects stored in S3 buckets.
B. Implement Object access control list (ACL) to deny unencrypted objects from being uploaded to the S3 bucket.
C. Implement Amazon S3 default encryption to make sure that any object being uploaded is encrypted before it is stored.
D. Implement Amazon Inspector to inspect objects uploaded to the S3 bucket to make sure that they are encrypted.
E. Implement S3 bucket policies to deny unencrypted objects from being uploaded to the buckets.
Answer: C, E
📘 Q7 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 Auto Scaling 그룹의 EC2 인스턴스에서 웹 애플리케이션을 호스팅 중
- ALB(Application Load Balancer) → CloudFront 오리진으로 구성됨
- 사용자가 웹 애플리케이션에서 무작위 로그아웃되는 문제가 발생
👉 SysOps 관리자가 해야 할 조치는 무엇일까? (2개 선택)
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. ALB 최소 미해결 요청 알골리즘으로 변경
→ 로드밸런싱 알고리즘 문제 아님 ❌ - B. CloudFront 캐시 정책에서 쿠키 전달 구성
→ 세션 정보는 보통 쿠키에 저장. CloudFront가 쿠키를 전달하지 않으면 세션 불일치 발생 ✅ - C. CloudFront에서 헤더 전달 구성
→ 일부 상황에서는 필요하지만, 여기서는 세션 쿠키 문제이므로 정답 아님 ❌ - D. ALB 리스너 규칙에서 그룹 수준 고정성(stickiness) 활성화
→ 리스너 단위 stickiness는 세밀하지 않음 ❌ - E. ALB 대상 그룹(Target Group)에서 고정 세션(sticky session) 활성화
→ 세션을 항상 같은 인스턴스로 라우팅해 로그아웃 문제 방지 ✅
✅ 정답: B, E
📝 쉬운 해설
- 웹 애플리케이션 로그인 세션은 쿠키 기반
- CloudFront가 쿠키를 오리진(ALB)으로 전달하지 않으면, ALB는 새 사용자처럼 취급 → 로그아웃 문제 발생
- ALB Target Group에서 Sticky Session을 켜면, 같은 사용자는 항상 동일 인스턴스로 연결됨 → 세션 유지
📊 Mermaid 시각화
U[사용자] --> CF[CloudFront]
CF -->|쿠키 전달| ALB[Application Load Balancer]
ALB --> TG[Target Group (Sticky Session ON)]
TG --> EC2A[EC2 인스턴스 A]
TG --> EC2B[EC2 인스턴스 B]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 세션 문제 = “쿠키 전달 + Sticky Session”
- CloudFront: 쿠키 전달 설정
- ALB Target Group: Sticky Session 활성화
Q7.
A company has a stateful web application that is hosted on Amazon EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group.
The instances run behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB) that has a single target group.
The ALB is configured as the origin in an Amazon CloudFront distribution.
Users are reporting random logouts from the web application.
Which combination of actions should a SysOps administrator take to resolve this problem? (Choose two)
A. Change to the least outstanding requests algorithm on the ALB target group.
B. Configure cookie forwarding in the CloudFront distribution cache behavior.
C. Configure header forwarding in the CloudFront distribution cache behavior.
D. Enable group-level stickiness on the ALB listener rule.
E. Enable sticky sessions on the ALB target group.
Answer: B, E
📘 Q12 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- SysOps 관리자가 CloudFormation 템플릿으로 VPC를 배포 완료
- 이제 AWS Organizations 내 여러 계정에 동일한 템플릿을 배포해야 함
- 운영 오버헤드 최소화가 목표
👉 어떤 방법이 가장 적절한가?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 마스터 계정에서 OrganizationAccountAccessRole IAM 역할 사용
→ 단일 계정 단위 배포라서 자동화/대규모 배포 불가 ❌ - B. 각 계정에서 Lambda + CreateStack API 호출
→ 코드 작성 필요, 오버헤드 큼 ❌ - C. 계정 목록을 관리하는 Lambda로 CreateStack API 호출
→ 여전히 커스텀 코드 필요 ❌ - D. 마스터 계정에서 CloudFormation StackSets 사용
→ 여러 계정·리전에 동시에 배포 가능 ✅
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudFormation Stack = 단일 계정, 단일 리전에만 리소스 생성
- StackSets = 여러 계정과 리전에 한 번에 배포 가능
- Organizations와 통합되어 있어 운영자가 코드 직접 작성할 필요 없음
- 운영 오버헤드 최소화 조건 충족
즉, 여러 계정에 공통 리소스를 배포해야 할 때는 StackSets가 정답!
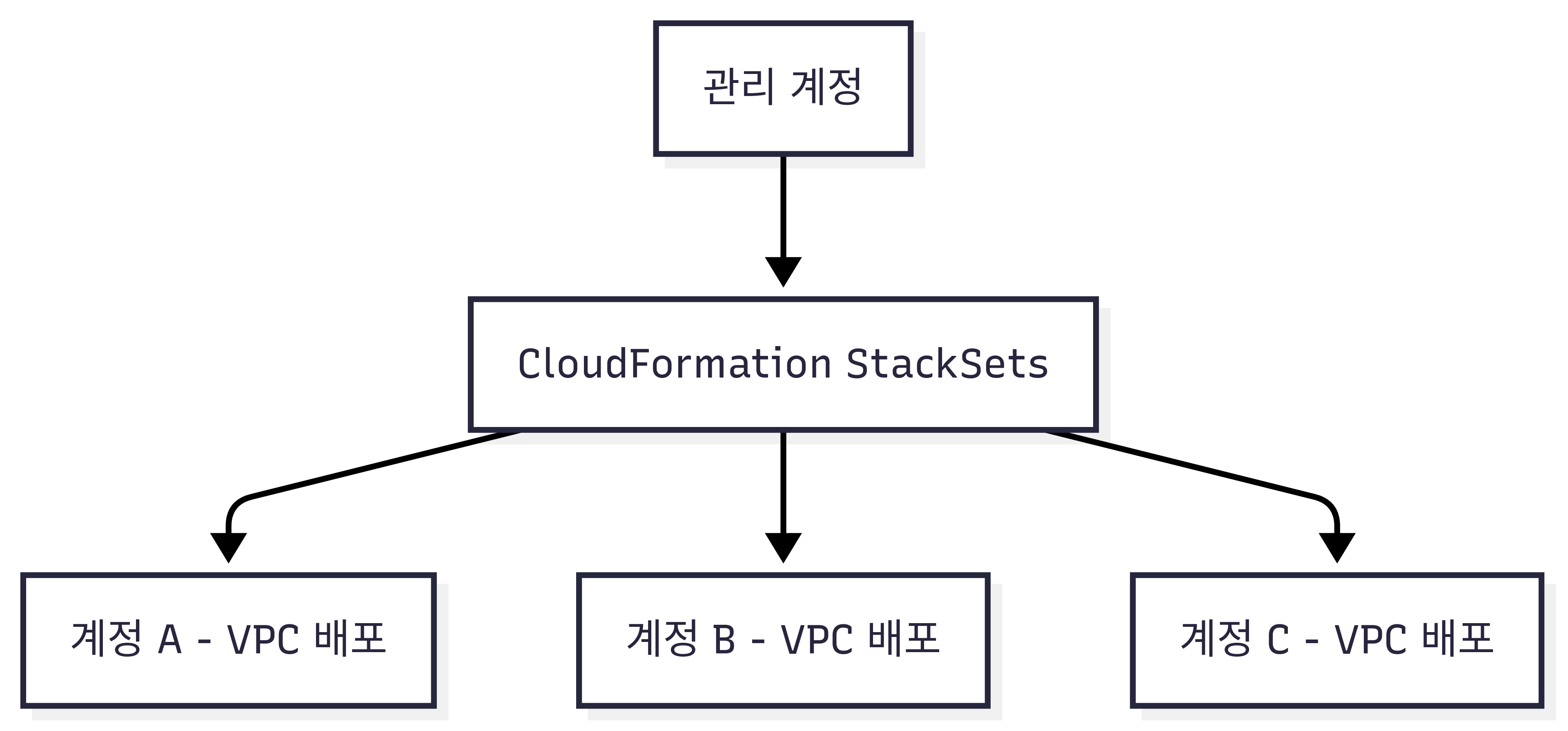
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[관리 계정] --> B[CloudFormation StackSets]
B --> C[계정 A - VPC 배포]
B --> D[계정 B - VPC 배포]
B --> E[계정 C - VPC 배포]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “여러 계정 + 여러 리전 = StackSets”
- 단일 계정/리전 = Stack
- 멀티 계정/리전 = StackSets
Q12.
A SysOps administrator has successfully deployed a VPC with an AWS CloudFormation template.
The SysOps administrator wants to deploy the same template across multiple accounts that are managed through AWS Organizations. Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
A. Assume the OrganizationAccountAccessRole IAM role from the management account.
Deploy the template in each of the accounts.
B. Create an AWS Lambda function to assume a role in each account.
Deploy the template by using the AWS CloudFormation CreateStack API call.
C. Create an AWS Lambda function to query for a list of accounts.
Deploy the template by using the AWS CloudFormation CreateStack API call.
D. Use AWS CloudFormation StackSets from the management account to deploy the template in each of the accounts.
Answer: D
📘 Q31 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- SysOps 관리자가 EC2 인스턴스에서 애플리케이션을 운영 중
- 애플리케이션이 DynamoDB 테이블에 접근할 수 있는 권한을 줘야 함
- 가장 적절한 방법은?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 액세스 키 생성 → EC2에 키 직접 넣기
→ 보안에 매우 취약 (키 유출 위험) ❌ - B. EC2 키 페어 생성 후 애플리케이션에 사용
→ 키 페어는 SSH 로그인용, DynamoDB 접근 권한과 무관 ❌ - C. IAM 사용자 생성 후 액세스 키 발급 → EC2에 할당
→ 가능하긴 하지만, 키 관리 문제와 보안 리스크 존재 ❌ - D. DynamoDB 접근 권한이 있는 IAM 역할(Role) 생성 → EC2 인스턴스 프로파일에 부여
→ 가장 안전하고 권장되는 방법 ✅
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- IAM Role = 임시 보안 자격 증명을 EC2에 자동으로 부여
- EC2 Instance Profile = 역할을 EC2에 붙이는 매개체
- 애플리케이션은 액세스 키를 직접 관리하지 않고, EC2 메타데이터 서비스(IMDS)로 권한을 얻음
💡 따라서 보안성이 가장 뛰어나고, AWS에서 공식적으로 권장하는 방식은 IAM Role 사용입니다.
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[EC2 인스턴스] --> B[EC2 인스턴스 프로파일]
B --> C[IAM Role (DynamoDB 접근 권한)]
C --> D[DynamoDB 테이블 접근]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 "EC2 → DynamoDB = IAM Role + Instance Profile"
- 액세스 키 = ❌ 위험
- 키 페어 = ❌ SSH 전용
- IAM Role = ✅ 보안 + 자동 인증
Q31.
A SysOps administrator is using Amazon EC2 instances to host an application.
The SysOps administrator needs to grant permissions for the application to access an Amazon DynamoDB table. Which solution will meet this requirement?
A. Create access keys to access the DynamoDB table. Assign the access keys to the EC2 instance profile.
B. Create an EC2 key pair to access the DynamoDB table. Assign the key pair to the EC2 instance profile.
C. Create an IAM user to access the DynamoDB table. Assign the IAM user to the EC2 instance profile.
D. Create an IAM role to access the DynamoDB table. Assign the IAM role to the EC2 instance profile.
Answer: D
📘 Q34 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 AWS Organizations를 사용해 여러 AWS 계정을 관리 중
- 기업 정책상 특정 리전만 사용 가능, 다른 리전에서는 EC2 인스턴스를 생성하면 안 됨
- 승인되지 않은 리전에서 EC2가 생성되지 않도록 운영 오버헤드가 최소인 방법을 찾아야 함
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. CloudTrail + EventBridge + Lambda로 차단
→ 가능은 하지만, 실행 후 탐지/종료 방식이라 완벽 차단 불가 ❌ - B. 각 계정별 IAM 정책으로 ec2:RunInstances 제한
→ 모든 계정마다 정책을 일일이 붙여야 해서 운영 오버헤드 큼 ❌ - C. 각 계정별 IAM 사용자/그룹에 경계 정책 연결
→ 여전히 계정별 관리 필요. 효율적이지 않음 ❌ - D. AWS Organizations의 서비스 제어 정책(SCP) 사용
→ 조직 전체(OU/루트)에 정책을 한 번만 적용하면 됨
→ “승인되지 않은 리전에서 ec2:RunInstances 거부” 가능 ✅
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- SCP(Service Control Policy) = AWS Organizations에서 제공하는 정책
- 모든 하위 계정에 공통 적용 가능
- 예: "Deny ec2:RunInstances if region != ap-northeast-2"
- 즉, 회사 정책을 중앙에서 통제하고, 계정별 세부 설정 불필요
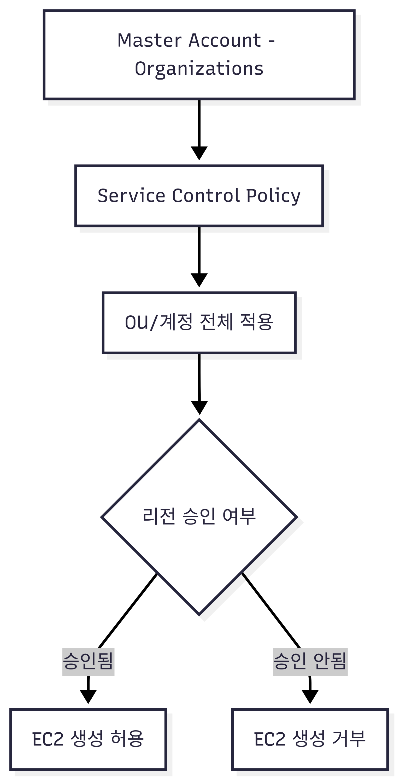
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[Master Account - Organizations] --> B[Service Control Policy (SCP)]
B --> C[OU / 계정 전체 적용]
C --> D{리전 승인 여부}
D -->|승인됨| E[EC2 생성 허용]
D -->|승인 안됨| F[EC2 생성 거부]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “계정 여러 개 + 중앙 통제 = SCP”
- IAM 정책 = 계정 단위
- SCP = 조직 전체 단위 (운영 효율 최고)
Q34.
A company uses AWS Organizations to manage multiple AWS accounts.
Corporate policy mandates that only specific AWS Regions can be used to store and process customer data.
A SysOps administrator must prevent the provisioning of Amazon EC2 instances in unauthorized Regions by anyone in the company.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
A. Configure AWS CloudTrail in all Regions to record all API activity.
Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule in all unauthorized Regions for ec2:RunInstances events.
Use AWS Lambda to terminate the launched EC2 instances.
B. In each AWS account, create a managed IAM policy that uses a Region condition to deny the ec2:RunInstances action in all unauthorized Regions. Attach this policy to all IAM groups in each AWS account. C. In each AWS account, create an IAM permissions boundary policy that uses a Region condition to deny the ec2:RunInstances action in all unauthorized Regions. Attach the permissions boundary policy to all IAM users in each AWS account.
D. Create a service control policy (SCP) in AWS Organizations to deny the ec2:RunInstances action in all unauthorized Regions. Attach this policy to the root level of the organization.
Answer: D
📘 Q35 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사 웹사이트 = CloudFront 배포 + us-east-1 S3 버킷에서 호스팅
- 요구사항 = DDoS 공격 방어 + 비율 제한(rate limiting) 기능 필요
👉 어떤 솔루션이 적합할까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. AWS WAF 웹 ACL을 CloudFront 배포에 연결 + 속도 기반(rate-based) 규칙 적용
→ CloudFront는 글로벌 서비스, DDoS 방어는 WAF + Shield Standard로 가능 ✅ - B. AWS WAF를 S3 버킷에 직접 연결
→ WAF는 S3에 직접 연결 불가, 오직 CloudFront, ALB, API Gateway 등에만 붙일 수 있음 ❌ - C. 차단 규칙만 사용해 WAF 적용
→ DDoS는 단순 차단 규칙보다 **비율 제한 규칙(rate limiting)**이 핵심. 요구사항 불충족 ❌ - D. S3 버킷에 연결된 WAF 적용
→ 다시 말하지만, S3에는 WAF 직접 연결 불가 ❌
✅ 정답: A
📝 쉬운 해설
- WAF(Web Application Firewall): CloudFront에 붙여서 특정 패턴/속도 기반 공격 차단 가능
- Shield Standard: CloudFront에 기본 포함되어 있어 DDoS 방어 지원
- 따라서 S3에 직접 보안 걸 수 없고, CloudFront + WAF 조합이 정답
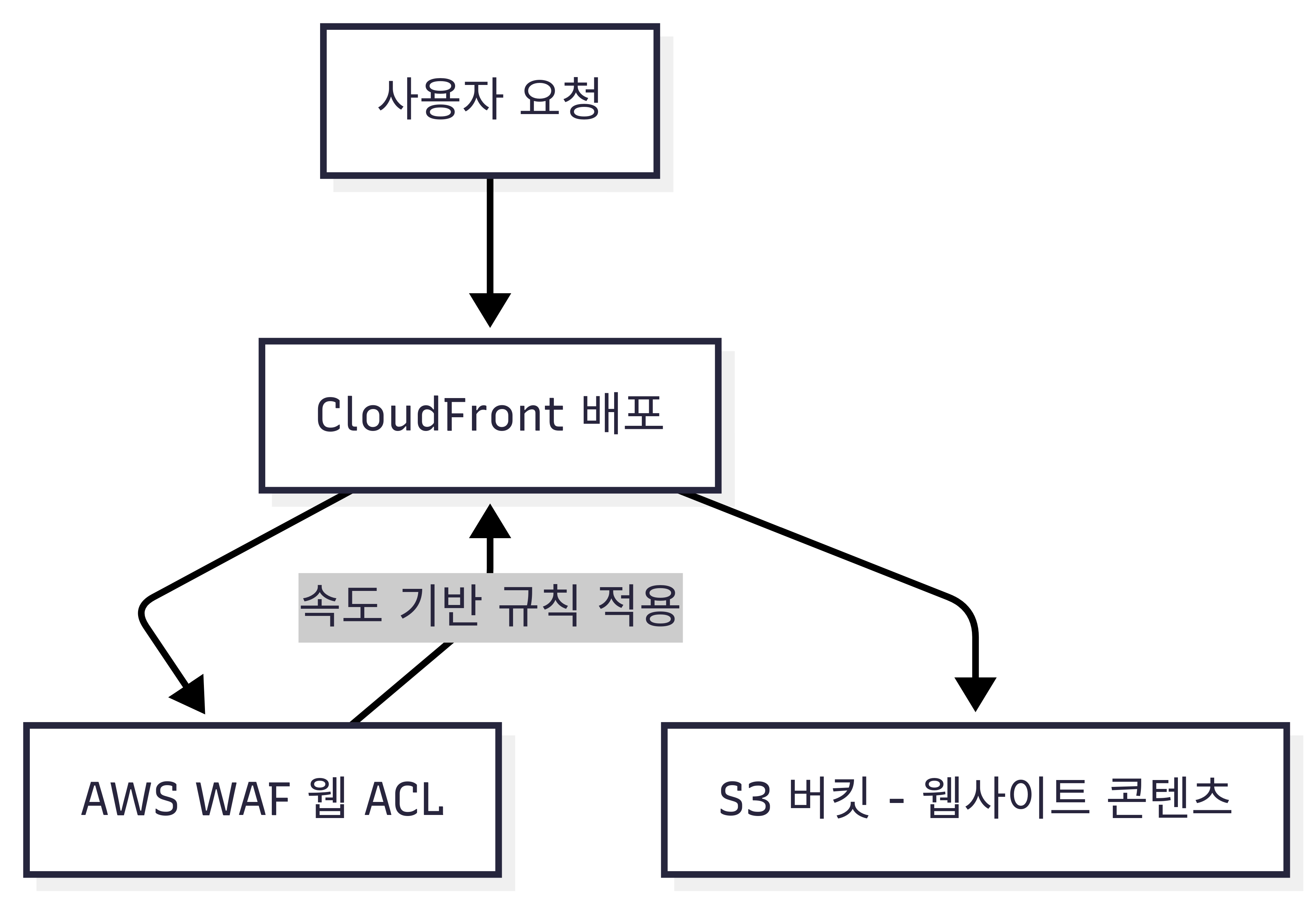
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[사용자 요청] --> CF[CloudFront 배포]
CF --> WAF[AWS WAF 웹 ACL]
WAF -->|속도 기반 규칙 적용| CF
CF --> S3[S3 버킷 - 웹사이트 콘텐츠]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “S3 보안은 직접 불가 → CloudFront + WAF”
- DDoS 방어 = 기본 Shield + WAF
- Rate limiting = WAF 규칙
Q35.
A company's public website is hosted in an Amazon S3 bucket in the us-east-1 Region behind an Amazon CloudFront distribution. The company wants to ensure that the website is protected from DDoS attacks.
A SysOps administrator needs to deploy a solution that gives the company the ability to maintain control over the rate limit at which DDoS protections are applied. Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Deploy a global-scoped AWS WAF web ACL with an allow default action.
Configure an AWS WAF rate-based rule to block matching traffic.
Associate the web ACL with the CloudFront distribution.
B. Deploy an AWS WAF web ACL with an allow default action in us-east-1.
Configure an AWS WAF rate-based rule to block matching traffic.
Associate the web ACL with the S3 bucket.
C. Deploy a global-scoped AWS WAF web ACL with a block default action.
Configure an AWS WAF rate-based rule to allow matching traffic.
Associate the web ACL with the CloudFront distribution.
D. Deploy an AWS WAF web ACL with a block default action in us-east-1.
Configure an AWS WAF rate-based rule to allow matching traffic.
Associate the web ACL with the S3 bucket.
Answer: A
📘 Q39 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- SysOps 관리자가 NAT 인스턴스를 NAT 게이트웨이로 마이그레이션
- 이후, 프라이빗 서브넷 EC2 애플리케이션이 인터넷에 접근 불가
👉 가능한 원인 2가지 선택
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 애플리케이션이 NAT 게이트웨이가 지원하지 않는 프로토콜을 사용
→ NAT 게이트웨이는 TCP/UDP만 지원, ICMP 같은 다른 프로토콜은 안 됨 ✅ - B. NAT 게이트웨이가 보안 그룹에 속하지 않음
→ NAT 게이트웨이는 ENI 기반이지만 보안 그룹을 사용하지 않음. 대신 NACL과 라우팅으로 제어됨 ❌ - C. NAT 게이트웨이가 지원되지 않는 가용 영역(AZ)에 존재
→ NAT 게이트웨이는 특정 AZ에서 생성해야 하고, 다른 AZ 리소스가 접근 가능함. 하지만 이 보기는 문제와 무관 ❌ - D. NAT 게이트웨이가 사용 불가능 상태
→ NAT 게이트웨이가 실패 상태거나 Elastic IP 미연결 시 인터넷 접근 불가 ✅ - E. 포트 포워딩 설정 문제
→ NAT 게이트웨이는 포트 포워딩 개념이 아님. ❌
✅ 정답: A, D
📝 쉬운 해설
- NAT Gateway 제한사항
- TCP/UDP 지원
- ICMP (ping) 같은 다른 프로토콜은 지원하지 않음
- 상태 확인
- NAT GW가 “사용 불가 상태”라면 트래픽 전달 불가
- 보통 Elastic IP 미연결, 라우팅 테이블 오류, 서브넷 문제가 원인
📊 Mermaid 시각화
EC2[Private EC2] --> RT[Route Table: 0.0.0.0/0]
RT --> NATGW[NAT Gateway]
NATGW --> IGW[Internet Gateway]
NATGW -->|비정상 상태 or 지원 안되는 프로토콜| ERR[인터넷 접근 불가]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “NAT GW 장애 원인 = 프로토콜 제한 + 상태 확인”
- TCP/UDP만 지원
- NAT 게이트웨이가 “사용 불가” 상태면 인터넷 연결 안 됨
Q39.
A SysOps administrator migrates NAT instances to NAT gateways. After the migration,
an application that is hosted on Amazon EC2 instances in a private subnet cannot access the internet.
Which of the following are possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two)
A. The application is using a protocol that the NAT gateway does not support.
B. The NAT gateway is not in a security group.
C. The NAT gateway is in an unsupported Availability Zone.
D. The NAT gateway is not in the Available state.
E. The port forwarding settings do not allow access to internal services from the internet.
Answer: A, D
📘 Q46 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사 웹 애플리케이션: ALB 뒤의 EC2에서 동작
- 백업 사이트: S3에 정적 웹사이트로 구성
- DNS: Route 53 사용
- 요구사항:
- ALB 기반 웹 애플리케이션이 장애나면 → 자동으로 S3 정적 웹사이트로 트래픽 전환
👉 어떤 작업 조합을 해야 할까? (2개 선택)
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 기본 장애 조치 라우팅 정책을 ALB로 설정
→ 백업 사이트 연결 고려 없음 ❌ - B. Lambda를 이용한 수동 장애 전환
→ 자동화 요구사항 충족 못 함 ❌ - C. 기본 장애 조치 라우팅 정책 레코드를 ALB로 설정, 상태 확인과 연결
→ 정상일 때는 ALB로 트래픽 전달 ✅ - D. 보조 장애 조치 라우팅 정책 레코드를 ALB로 설정
→ 백업은 ALB가 아니라 S3여야 함 ❌ - E. 보조 장애 조치 라우팅 정책 레코드를 S3 정적 웹사이트로 설정
→ ALB 장애 시 자동으로 S3로 트래픽 전환 ✅
✅ 정답: C, E
📝 쉬운 해설
- Route 53 Failover Routing을 사용
- Primary = ALB
- Secondary = S3 정적 웹사이트
- Route 53이 Health Check로 ALB 상태를 감시
- 장애 발생 시 자동으로 S3 백업 사이트로 전환
📊 Mermaid 시각화
U[사용자] --> R53[Route 53 - Failover Routing]
R53 -->|ALB 정상| ALB[Application Load Balancer → EC2]
R53 -->|ALB 장애| S3[S3 정적 웹사이트 (백업)]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “ALB Primary + S3 Secondary = Route 53 Failover”
- ALB = 메인 서비스
- S3 = 백업 사이트
- Route 53 Health Check로 자동 전환
Q46.
A company hosts a web application on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB).
The company uses Amazon Route 53 to route traffic.
The company also has a static website that is configured in an Amazon S3 bucket.
A SysOps administrator must use the static website as a backup to the web application.
The failover to the static website must be fully automated.
Which combination of actions will meet these requirements? (Choose two)
A. Create a primary failover routing policy record.
Configure the value to be the ALB.
B. Create an AWS Lambda function to switch from the primary website
to the secondary website when the health check fails.
C. Create a primary failover routing policy record.
Configure the value to be the ALB.
Associate the record with a Route 53 health check.
D. Create a secondary failover routing policy record.
Configure the value to be the static website.
Associate the record with a Route 53 health check.
E. Create a secondary failover routing policy record.
Configure the value to be the static website.
Answer: C, E
📘 Q47 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- Amazon EC2 인스턴스에서 데이터 분석 애플리케이션 실행 중
- SysOps 관리자가 CloudWatch Agent에서 수집하는 메트릭에 **사용자 지정 차원(Custom Dimension)**을 추가해야 함
👉 어떤 방법이 올바른가?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. CloudWatch Agent + 사용자 지정 스크립트
→ 가능은 하지만 번거롭고 관리 부담 큼 ❌ - B. EventBridge 규칙 + SNS 전송
→ 알림/이벤트 처리용. 메트릭에 차원 추가와는 무관 ❌ - C. CloudTrail + CloudWatch Logs + Lambda
→ CloudTrail은 API 호출 기록용. 메트릭 차원 추가와는 관계 없음 ❌ - D. CloudWatch Agent 설정 파일에 append_dimensions 필드 추가
→ 가장 올바른 방법 ✅
→ 예: {"append_dimensions": {"InstanceId": "${aws:InstanceId}"}}
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudWatch Agent 설정 파일(amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json)에는
→ metrics_collected (수집할 메트릭)
→ append_dimensions (추가할 사용자 지정 차원) - 예를 들어, 각 인스턴스의 InstanceId, AutoScalingGroupName 등을 차원으로 붙일 수 있음
- 이렇게 하면 메트릭 분석/필터링이 훨씬 쉬워짐
📊 Mermaid 시각화
EC2[EC2 인스턴스] --> CWA[CloudWatch Agent]
CWA -->|메트릭 수집 + append_dimensions| CW[CloudWatch Metrics]
CW --> D[사용자 지정 차원 추가된 메트릭 저장]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 CloudWatch 메트릭에 사용자 정의 차원 추가 = append_dimensions
- Agent 설정 파일에서 지정
- InstanceId, ASG 이름 같은 정보 자동 추가 가능
Q47.
A data analytics application is running on an Amazon EC2 instance.
A SysOps administrator must add custom dimensions to the metrics collected by the Amazon CloudWatch agent. How can the SysOps administrator meet this requirement?
A. Create a custom shell script to extract the dimensions and collect the metrics using the Amazon CloudWatch agent.
B. Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule to evaluate the required custom dimensions and send the metrics to Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS).
C. Create an AWS Lambda function to collect the metrics from AWS CloudTrail and send the metrics to an Amazon CloudWatch Logs group.
D. Create an append_dimensions field in the Amazon CloudWatch agent configuration file to collect the metrics.
Answer: D
📘 Q51 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- SysOps 관리자가 아래와 같은 CloudFormation 템플릿을 사용하여 EC2 인스턴스를 생성하려고 함
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: 'Creates an EC2 Instance'
Resources:
EC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: ami-79fd7eee
InstanceType: m5n.large
SubnetId: subnet-1abc3d3fg
PrivateDnsName: ip-10-24-34-0.ec2.internal
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName} Instance"
👉 스택 생성이 실패하는 이유는 무엇일까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 출력(Outputs) 섹션 없음
→ Outputs는 선택 사항. 없어도 스택 생성 가능 ❌ - B. 매개변수(Parameters) 섹션 없음
→ Parameters도 선택 사항. 없어도 문제 없음 ❌ - C. PrivateDnsName 속성은 CloudFormation에서 설정할 수 없음
→ ✅ 올바른 답변. PrivateDnsName은 EC2 생성 시 AWS에서 자동으로 할당하는 값이지, 사용자가 템플릿에 직접 지정 불가 ✅ - D. VPC 지정 없음
→ SubnetId를 지정했기 때문에 VPC도 자동으로 연계됨. 문제 아님 ❌
✅ 정답: C
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudFormation에서 허용되지 않는 속성을 사용했기 때문
- EC2의 PrivateDnsName은 AWS가 인스턴스 시작 시 자동 생성하는 값
- 따라서 CloudFormation 템플릿에서 해당 속성을 수동으로 지정하면 스택 생성 실패 발생
📊 Mermaid 시각화
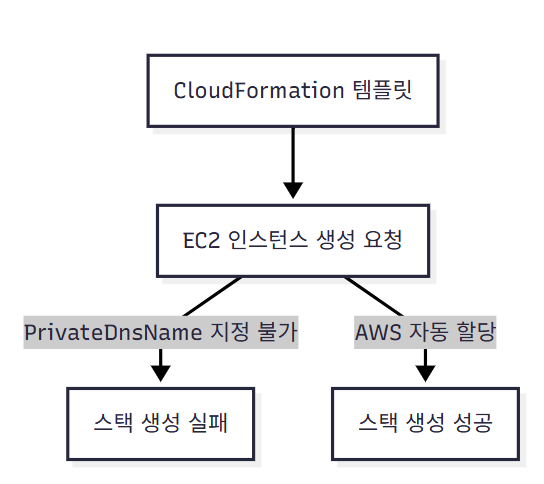
CF[CloudFormation 템플릿] --> EC2[EC2 인스턴스 생성 요청]
EC2 -->|PrivateDnsName 지정 불가| Error[스택 생성 실패]
EC2 -->|AWS 자동 할당| OK[스택 생성 성공]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “CloudFormation에서 EC2 PrivateDnsName은 자동 설정”
- 수동 지정 ❌ → 오류 발생
- AWS가 자동 할당 ✅
Q51.
A SysOps administrator is examining the following AWS CloudFormation template:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: 'Creates an EC2 Instance'
Resources:
EC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: ami-79fd7eee
InstanceType: m5n.large
SubnetId: subnet-1abc3d3fg
PrivateDnsName: ip-10-24-34-0.ec2.internal
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: !Sub "${AWS::StackName} Instance"
Why will the stack creation fail?
A. The Outputs section of the CloudFormation template was omitted.
B. The Parameters section of the CloudFormation template was omitted.
C. The PrivateDnsName cannot be set from a CloudFormation template.
D. The VPC was not specified in the CloudFormation template.
Answer: C
📘 Q52 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 새 애플리케이션: EC2 인스턴스에서 실행
- 데이터베이스: Amazon RDS 인스턴스
- 배포 후 애플리케이션이 실패하고,
에러 로그: Error Establishing a Database Connection
👉 가능한 원인은? (2개 선택)
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. DB 보안 그룹에 송신 규칙 없음
→ 송신 규칙은 기본적으로 모든 아웃바운드 허용. 일반적으로 문제 원인 아님 ❌ - B. 인증서 문제
→ TLS 인증서 신뢰 관련. 여기서는 연결 자체가 안 되므로 무관 ❌ - C. DB 보안 그룹에 EC2 → DB로의 수신 규칙 없음
→ ✅ 올바른 원인. DB 보안 그룹에서 EC2 보안 그룹/서브넷을 허용해야 연결 가능 - D. EC2 애플리케이션의 포트가 DB 포트와 불일치
→ ✅ 올바른 원인. 예: DB는 3306인데 애플리케이션 설정이 3307이면 연결 불가 - E. RDS가 아직 생성 중
→ 문제에서 이미 "쿼리할 수 있다"고 했으므로 무관 ❌
✅ 정답: C, D
📝 쉬운 해설
- DB 연결 실패 주요 원인
- DB 보안 그룹(Security Group)에서 EC2 인스턴스 접근을 허용하지 않음
- 앱에서 사용하는 DB 포트 설정이 잘못됨
- EC2 → RDS 연결 성공 조건
- 올바른 포트 (MySQL=3306, PostgreSQL=5432 등)
- DB SG에서 EC2 SG 또는 CIDR 허용
📊 Mermaid 시각화
```mermaid
EC2[애플리케이션 EC2] -->|3307 잘못된 포트| ERR1[연결 실패]
EC2 -->|3306 OK| SG[DB Security Group]
SG -->|허용 안됨| ERR2[연결 거부]
SG -->|허용됨| RDS[Amazon RDS DB]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “DB 연결 안 될 때는? SG 규칙 + 포트 확인”
- SG 인바운드 확인
- 앱 DB 포트 확인
Q52.
A new application runs on Amazon EC2 instances and accesses data in an Amazon RDS database instance. When fully deployed in production, the application fails.
The database can be queried from a console on a bastion host.
When looking at the web server logs, the following error is repeated multiple times:
*** Error Establishing a Database Connection Which of the following may be causes of the connectivity problems? (Choose two)
A. The security group for the database does not have the appropriate egress rule from the database to the web server.
B. The certificate used by the web server is not trusted by the RDS instance.
C. The security group for the database does not have the appropriate ingress rule from the web server to the database.
D. The port used by the application developer does not match the port specified in the RDS configuration.
E. The database is still being created and is not available for connectivity.
Answer: C, D
📘 Q55 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 CloudFront 배포를 통해 웹사이트를 제공
- 모든 트래픽 로그는 중앙에서 저장되어야 함
- 저장 시 모든 데이터는 반드시 암호화되어야 함
👉 어떤 솔루션이 이 요구사항을 충족할까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. KMS CMK + OpenSearch
→ OpenSearch는 검색/로그 분석 서비스, CloudFront 로그 저장소로 적합하지 않음 ❌ - B. AES-256 + OpenSearch
→ 역시 저장은 가능하지만 중앙 저장/암호화 로그 저장소로는 비효율적 ❌ - C. AES-256 서버 측 암호화(SSE-S3) 적용된 S3 버킷에 CloudFront 로그 저장
→ CloudFront 액세스 로그를 S3로 저장 가능
→ S3에서 AES-256 기본 암호화 적용하면 저장 시 자동 암호화 ✅ - D. KMS 암호화된 S3 버킷 + CloudFront 로그 저장
→ 가능은 하지만 요구사항은 단순히 “모든 데이터가 암호화”
→ 기본 AES-256로 충분, KMS는 과도한 옵션 ❌
✅ 정답: C
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudFront는 액세스 로그를 S3 버킷에 저장 가능
- S3는 저장 시 자동 암호화 기능 제공
- SSE-S3 (AES-256): 간단하고 관리 부담 적음
- SSE-KMS: 더 세밀한 키 관리 필요할 때 사용
- 문제 요구사항 = 저장 시 반드시 암호화 → AES-256 기본 암호화로 충족
📊 Mermaid 시각화
U[사용자 요청] --> CF[CloudFront]
CF --> Logs[Access Logs]
Logs --> S3[S3 버킷 (SSE-S3, AES-256 암호화)]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “CloudFront 로그 중앙 저장 = S3 + AES-256”
- CloudFront 로그 저장 = 항상 S3
- 데이터 암호화 = 기본 AES-256로 충분
Q55.
A company uses an Amazon CloudFront distribution to deliver its website.
Traffic logs for the website must be centrally stored, and all data must be encrypted at rest.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A. Create an Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service) domain with internet access and server-side encryption that uses the default AWS managed customer master key (CMK).
Configure CloudFront to use the Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service) domain as a log destination.
B. Create an Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service) domain with VPC access and server-side encryption that uses AES-256. Configure CloudFront to use the Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service) domain as a log destination.
C. Create an Amazon S3 bucket that is configured with default server-side encryption that uses AES-256. Configure CloudFront to use the S3 bucket as a log destination.
D. Create an Amazon S3 bucket that is configured with no default encryption.
Enable encryption in the CloudFront distribution, and use the S3 bucket as a log destination.
Answer: C
📘 Q62 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 SysOps 관리자에게 CloudTrail 로그 파일이 생성된 후 변조되지 않았는지 확인하도록 요청
- IAM을 사용해 특정 트레일에 대한 액세스를 제한해야 함
- 요구사항: 로그 파일의 무결성 검증 기능 필요
👉 어떤 방법이 가장 효율적인가?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. Lambda + EventBridge + DynamoDB로 MD5 해시 검증
→ 가능은 하지만 너무 복잡하고 운영 오버헤드 큼 ❌ - B. Lambda로 CloudTrail 전달 이벤트마다 해시 계산 후 S3에 저장
→ 역시 사용자 정의 코드 필요, 비효율적 ❌ - C. S3 버킷 정책으로 IAM 권한 제어
→ 권한 제어는 되지만, 파일 무결성(변조 여부) 검증은 불가 ❌ - D. CloudTrail 로그 파일 무결성 검증 기능 활성화
→ AWS에서 제공하는 기본 기능 ✅
→ CloudTrail은 각 로그 파일에 서명(Signature)과 다이제스트(Digest) 파일을 제공
→ 보안 팀이 이를 통해 로그 파일이 변조되지 않았는지 확인 가능
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- CloudTrail은 옵션으로 **로그 파일 무결성 검증(File Integrity Validation)**을 지원
- 활성화 시 각 로그 파일에 대해 SHA-256 해시 + 디지털 서명을 함께 제공
- 보안팀은 이를 사용해 로그가 중간에 변조되었는지 확인 가능
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[CloudTrail 로그 파일] --> B[SHA-256 해시 생성]
B --> C[디지털 서명 + Digest 파일 생성]
C --> S3[S3에 저장]
S3 --> Sec[보안팀 검증: 변조 여부 확인]

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “CloudTrail 로그 변조 방지 = 무결성 검증 기능 ON”
- Digest 파일 + 서명 → 변조 여부 추적 가능
- Lambda 같은 커스텀 검증 불필요
Q62.
A company asks a SysOps administrator to ensure that AWS CloudTrail files are not tampered with after they are created. Currently, the company uses AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to restrict access to specific trails. The company's security team needs the ability to trace the integrity of each file.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
A. Create an Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) rule that invokes an AWS Lambda function when a new file is delivered. Configure the Lambda function to compute an MD5 hash check on the file and store the result in an Amazon DynamoDB table. The security team can use the values that are stored in DynamoDB to verify the integrity of the delivered files.
B. Create an AWS Lambda function that is invoked each time a new file is delivered to the CloudTrail bucket. Configure the Lambda function to compute an MD5 hash check on the file and store the result as a tag in an Amazon 53 object. The security team can use the information in the tag to verify the integrity of the delivered files. C. Enable the CloudTrail file integrity feature on an Amazon S3 bucket. Create an IAM policy that grants the security team access to the file integrity logs that are stored in the S3 bucket.
D. Enable the CloudTrail file integrity feature on the trail. The security team can use the digest file that is created by CloudTrail to verify the integrity of the delivered files.
Answer: D
📘 Q63 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- AWS 클라우드 인프라에서 조직에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 이벤트가 발생했을 때,
- 어떤 AWS 서비스를 통해 내 리소스에 직접적인 영향 여부를 확인할 수 있을까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. AWS Service Health Dashboard
→ AWS 전체 리전/서비스 상태를 보여줌 (공용 대시보드)
→ 내 계정 리소스에 영향이 있는지는 알려주지 않음 ❌ - B. AWS Trusted Advisor
→ 비용 최적화, 보안, 성능, 제한(Quota) 점검 도구
→ 이벤트 영향과는 무관 ❌ - C. AWS Personal Health Dashboard
→ 내 계정과 리소스에 직접 영향이 있는 이벤트를 보여줌 ✅
→ 예: 특정 리전 EC2 장애가 내 인스턴스에 영향을 주는지 확인 가능 - D. AWS Systems Manager
→ 인스턴스/리소스 운영 관리 도구
→ 이벤트 모니터링 서비스 아님 ❌
✅ 정답: C
📝 쉬운 해설
- Service Health Dashboard = 전 세계 AWS 서비스 상태 (공통, 누구나 확인 가능)
- Personal Health Dashboard = 내 계정 리소스에 실제 영향이 있는 이벤트만 표시 (맞춤형)
즉, "조직에 영향을 주는 이벤트 확인" 문제에서는 항상 Personal Health Dashboard가 정답!
📊 Mermaid 시각화
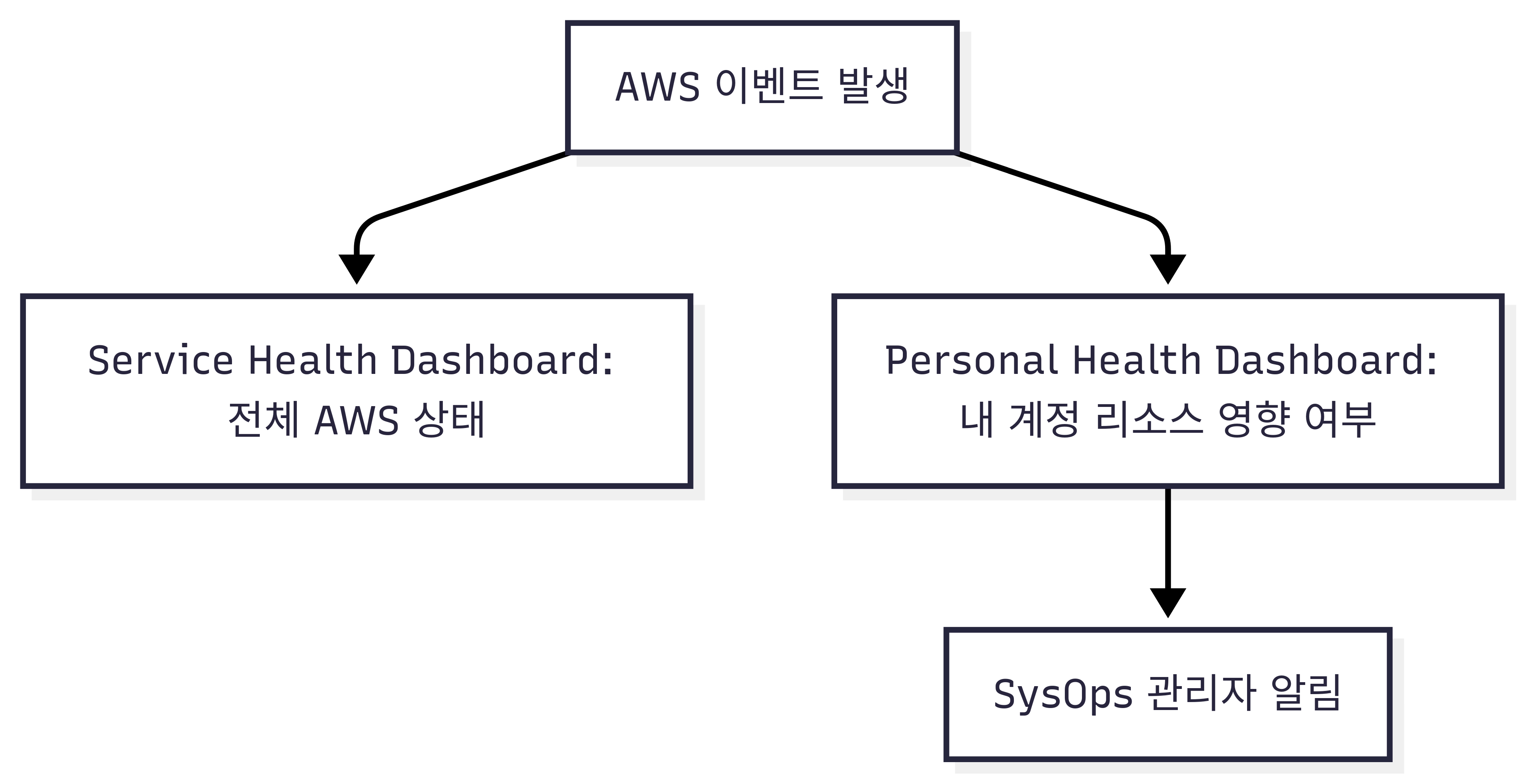
A[AWS 이벤트 발생] --> B[Service Health Dashboard: 전체 AWS 상태]
A --> C[Personal Health Dashboard: 내 계정 리소스 영향 여부]
C --> D[SysOps 관리자 알림]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “전체 상태 = Service, 내 리소스 영향 = Personal”
- Service Health Dashboard = 전 세계 상황
- Personal Health Dashboard = 내 계정 영향
Q63.
When the AWS Cloud infrastructure experiences an event that may impact an organization,
which AWS service can be used to see which of the organization's resources are affected?
A. AWS Service Health Dashboard
B. AWS Trusted Advisor
C. AWS Personal Health Dashboard
D. AWS Systems Manager
Answer: C
📘 Q66 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 웹사이트: Amazon S3 정적 웹사이트 호스팅
- DNS: Route 53에서 도메인 이름(www.example.com)을 설정해 S3 버킷에 매핑
- 그런데 설정 후 도메인 접속이 안 되고, S3 정적 웹사이트 기본 도메인(예: s3-website-...amazonaws.com)만 표시됨
👉 원인은 무엇일까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 먼저 CloudFront를 구성해야 한다
→ S3 정적 웹사이트는 CloudFront 없어도 동작 가능. 필수 조건 아님 ❌ - B. Route 53 레코드에 IAM 권한 필요
→ Route 53 레코드는 DNS 리졸빙만 담당, IAM 권한과 무관 ❌ - C. Route 53 레코드는 동일 리전에 있어야 한다
→ Route 53은 글로벌 서비스, 리전 무관 ❌ - D. S3 버킷 이름이 Route 53 도메인 이름과 반드시 일치해야 한다
→ 정답 ✅
→ 예: 도메인 이름이 www.example.com이면, S3 버킷 이름도 **www.example.com**이어야 함
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- S3 정적 웹사이트 호스팅 시 버킷 이름 = 도메인 이름이어야 함
- 예시:
- 도메인: www.example.com
- S3 버킷 이름: www.example.com
- 그렇지 않으면 Route 53에서 Alias 레코드 연결 시 인식되지 않아 접속 불가
📊 Mermaid 시각화
```mermaid
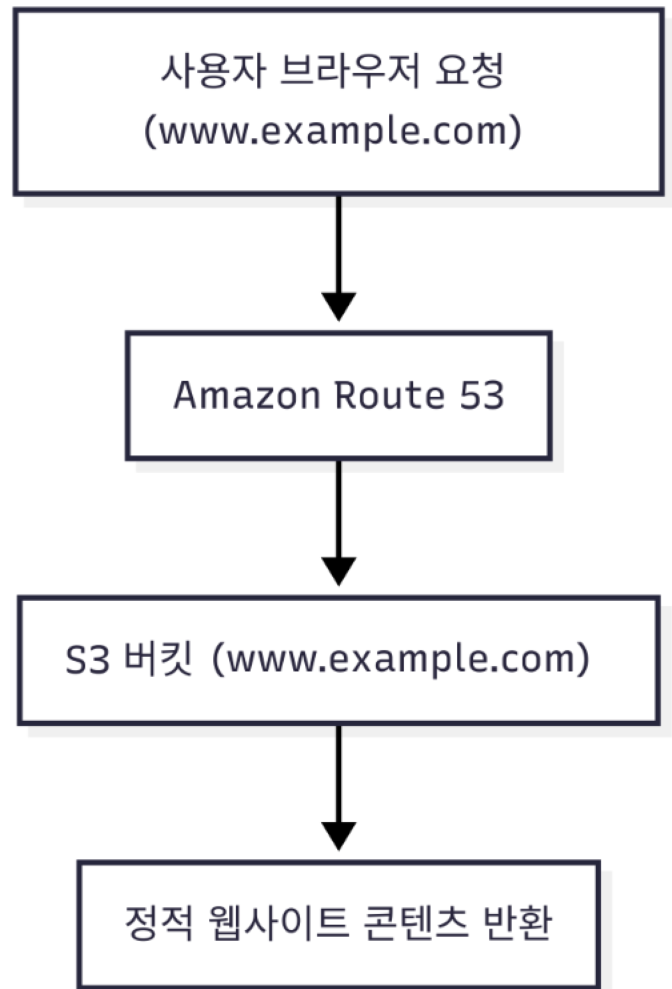
User[사용자 브라우저 요청 http://www.example.com] --> R53[Amazon Route 53]
R53 --> S3[S3 버킷: http://www.example.com]
S3 --> Content[정적 웹사이트 콘텐츠 반환]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “S3 정적 웹 호스팅 = 버킷 이름 = 도메인 이름”
- example.com → 버킷 이름도 example.com
- www.example.com → 버킷 이름도 www.example.com
Q66.
A SysOps administrator is trying to set up an Amazon Route 53 domain name to route traffic to a website hosted on Amazon S3.
The domain name of the website is www.example.com and the S3 bucket name DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET.
After the record set is set up in Route 53, the domain name www.anycompany.com does not seem to work,
and the static website is not displayed in the browser. Which of the following is a cause of this?
A. The S3 bucket must be configured with Amazon CloudFront first.
B. The Route 53 record set must have an IAM role that allows access to the S3 bucket.
C. The Route 53 record set must be in the same region as the S3 bucket.
D. The S3 bucket name must match the record set name in Route 53.
Answer: D
📘 Q78 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 글로벌 기업, 5개 리전에서 EC2 인스턴스 운영 중
- SysOps 관리자는 특정 태그가 없는 EC2 인스턴스를 찾아내야 함
- 회사는 인스턴스 ID와 태그를 보여주는 출력물이 필요
👉 가장 운영상 효율적인 방법은?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 태그 기반 리소스 그룹 생성
→ 태그가 없는 리소스는 그룹화할 수 없음 ❌ - B. Trusted Advisor 사용
→ Trusted Advisor는 비용/보안/제한 권고 제공, 태그 기반 인스턴스 리포트는 제공하지 않음 ❌ - C. 비용 탐색기(Cost Explorer)
→ 비용/사용량 기반 분석 도구, 태그 없는 인스턴스 구분 용도 아님 ❌ - D. AWS 리소스 그룹(Tag Editor) 사용
→ 여러 리전에 걸쳐 모든 EC2 인스턴스와 태그를 조회 가능 ✅
→ 태그가 없는 리소스도 쉽게 식별 가능
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- Tag Editor (리소스 그룹) = 여러 리전에 걸쳐 리소스의 태그 현황을 검색/관리할 수 있는 도구
- 필터로 EC2 인스턴스 리소스를 선택 → 태그 여부 확인 가능
- 태그가 없는 인스턴스도 결과에서 보여주기 때문에 요구사항 충족
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[SysOps 관리자] --> B[AWS Resource Groups - Tag Editor]
B -->|리전 전체 검색| C[EC2 인스턴스 조회]
C -->|태그 존재| D[정상 태깅된 인스턴스]
C -->|태그 없음| E[태그 미적용 인스턴스 식별]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “여러 리전 태그 관리 = Tag Editor”
- Trusted Advisor ❌ (권장사항)
- Cost Explorer ❌ (비용 분석)
- Tag Editor ✅ (태그 현황 관리/조회)
Q78.
A global company operates out of five AWS Regions.
A SysOps administrator wants to identify all the company's tagged and untagged Amazon EC2 instances.
The company requires the output to display the instance ID and tags.
What is the MOST operationally efficient way for the SysOps administrator to meet these requirements?
A. Create a tag-based resource group in AWS Resource Groups.
B. Use AWS Trusted Advisor. Export the EC2 On-Demand Instances check results from Trusted Advisor.
C. Use Cost Explorer. Choose a service type of EC2-Instances, and group by Resource.
D. Use Tag Editor in AWS Resource Groups. Select all Regions, and choose a resource type of AWS::EC2::Instance.
Answer: D
📘 Q84 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 us-east-1 리전의 한 가용 영역(AZ)에 두 개의 EC2 인스턴스를 실행 중
- SysOps 관리자는 이 중 하나를 다른 가용 영역(AZ) 으로 마이그레이션해야 함
👉 어떤 방법이 적절할까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. 인스턴스를 다른 가용 영역으로 복사 후 원본 종료
→ EC2는 단순히 “복사”로 다른 AZ로 옮길 수 없음 ❌ - B. EC2 인스턴스에서 AMI(Amazon Machine Image) 생성 후, 이를 다른 AZ에서 시작
→ 올바른 절차 ✅
→ AMI로 동일한 설정의 새 인스턴스를 다른 AZ에 배포 가능 - C. AWS CLI로 인스턴스를 직접 다른 AZ로 이동
→ EC2 인스턴스는 “이동” 개념이 없음. 새로 시작해야 함 ❌ - D. 인스턴스 중지 후 AZ 수정
→ AZ는 변경 불가능. 중지 후 재시작해도 같은 AZ에 생성됨 ❌
✅ 정답: B
📝 쉬운 해설
- EC2 인스턴스는 생성된 가용 영역을 바꿀 수 없음
- 따라서 AMI를 생성 → 원하는 AZ에서 새로운 인스턴스를 시작해야 함
- 원본 인스턴스는 종료할 수 있음 (옵션)
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[원본 EC2 인스턴스 (AZ-a)] --> B[AMI 생성]
B --> C[새로운 AZ-b에서 EC2 시작]
C --> D[애플리케이션 마이그레이션 완료]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “AZ 변경 = AMI 만들어 새로 시작”
- 이동 ❌
- 중지 후 재시작 ❌
- AMI 생성 → 새 인스턴스 시작 ✅
Q84.
A company runs a multi-tier web application with two Amazon EC2 instances in one Availability Zone in the us-east-1 Region. A SysOps administrator must migrate one of the EC2 instances to a new Availability Zone.
Which solution will accomplish this?
A. Copy the EC2 instance to a different Availability Zone. Terminate the original instance.
B. Create an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) from the EC2 instance and launch it in a different Availability Zone. Terminate the original instance.
C. Move the EC2 instance to a different Availability Zone using the AWS CLI.
D. Stop the EC2 instance, modify the Availability Zone, and start the instance.
Answer: B
📘 Q85 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- 회사는 트래픽 증가 대비 → EC2 인스턴스 집합 확장 계획
- SysOps 관리자가 인스턴스 추가 시도 → InstanceLimitExceeded 오류 발생
👉 이 오류를 해결하려면 어떻게 해야 할까?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. VPC에 추가 CIDR 블록 할당
→ 네트워크 IP 공간 부족 문제 해결 방법, 이번 문제와 무관 ❌ - B. 다른 가용 영역(AZ)에서 EC2 시작
→ AZ를 바꿔도 계정의 인스턴스 한도는 동일. 오류 해결 불가 ❌ - C. 다른 VPC에서 새 인스턴스 시작
→ VPC를 바꿔도 계정 한도는 동일. 해결책 아님 ❌ - D. 서비스 할당량(Service Quotas)에서 EC2 인스턴스 한도 증가 요청
→ 정답 ✅
→ InstanceLimitExceeded 오류는 계정의 **EC2 서비스 할당량(Soft Limit)**을 초과했을 때 발생
→ 콘솔(Service Quotas)이나 AWS Support로 증가 요청 가능
✅ 정답: D
📝 쉬운 해설
- AWS 계정에는 리소스별 기본 서비스 한도가 있음
- 예: 리전별 EC2 인스턴스 수 제한
- InstanceLimitExceeded는 바로 이 한도를 초과했을 때 발생하는 오류
- 해결책 = 할당량 증가 요청(Quota Increase)
📊 Mermaid 시각화
A[SysOps: EC2 인스턴스 추가 시도] --> B[InstanceLimitExceeded 오류]
B --> C[원인: EC2 서비스 한도 초과]
C --> D[해결: Service Quotas에서 한도 증가 요청]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 “InstanceLimitExceeded = Service Quotas 요청”
- 네트워크 문제 아님 ❌
- AZ/VPC 바꿔도 동일 ❌
- Service Quotas에서 증가 요청 ✅
Q85.
A company is expanding its fleet of Amazon EC2 instances before an expected increase of traffic.
When a SysOps administrator attempts to add more instances, an InstanceLimitExceeded error is returned.
What should the SysOps administrator do to resolve this error?
A. Add an additional CIDR block to the VPC.
B. Launch the EC2 instances in a different Availability Zone.
C. Launch new EC2 instances in another VPC.
D. Use Service Quotas to request an EC2 quota increase.
Answer: D
📘 Q87 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- EC2 인스턴스가 VPC 안에서 실행 중
- 애플리케이션은 mssql.example.com (온프레미스 SQL Server) DB에 연결해야 함
- 그런데 VPC 내부 EC2 인스턴스는 해당 DNS 이름을 확인하지 못함
👉 이 문제를 해결하는 방법은?
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. Route 53 Resolver 인바운드 엔드포인트 + 전달 규칙
→ 인바운드는 온프레미스에서 AWS로 오는 DNS 쿼리 처리용 ❌ - B. Route 53 Resolver 인바운드 엔드포인트 + 시스템 규칙
→ 인바운드는 여전히 방향이 반대. 이번 문제와 무관 ❌ - C. Route 53 Resolver 아웃바운드 엔드포인트 + 전달 규칙
→ EC2 → 온프레미스 DNS로 쿼리 전송 가능 ✅
→ VPC와 연결 후 example.com 도메인에 대한 전달 규칙 작성 - D. Route 53 Resolver 아웃바운드 엔드포인트 + 시스템 규칙
→ 시스템 규칙이 아니라 전달 규칙을 사용해야 함 ❌
✅ 정답: C
📝 쉬운 해설
- 인바운드 엔드포인트: 온프레미스 → AWS VPC로 DNS 요청 보낼 때 필요
- 아웃바운드 엔드포인트: AWS VPC → 온프레미스 DNS 서버로 요청 보낼 때 필요
- 이번 문제는 EC2(VPC) → 온프레미스 DNS 쿼리라서 아웃바운드 엔드포인트가 정답
📊 Mermaid 시각화
```mermaid
EC2[EC2 in VPC] --> R53[Route 53 Resolver 아웃바운드 엔드포인트]
R53 --> DNS[On-Prem DNS Server]
DNS --> MSSQL[On-Prem MSSQL Database]
🎯 암기 팁
👉 DNS 쿼리 방향 기억하기
- 온프레미스 → AWS = 인바운드
- AWS VPC → 온프레미스 = 아웃바운드
Q87.
An application is running on an Amazon EC2 instance in a VPC with the default DHCP option set. The application connects to an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server database with the DNS name mssql.example.com.
The application is unable to resolve the database DNS name.
Which solution will fix this problem?
A. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound endpoint. Add a forwarding rule for the domain example.com. Associate the forwarding rule with the VPC.
B. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound endpoint. Add a system rule for the domain example.com. Associate the system rule with the VPC.
C. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint. Add a forwarding rule for the domain example.com. Associate the forwarding rule with the VPC.
D. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint. Add a system rule for the domain example.com. Associate the system rule with the VPC.
Answer: C
📘 Q94 문제 정리
🔹 문제 요약
- SysOps 관리자는 여러 IAM 정책을 IAM 사용자에게 연결해 AWS 서비스 접근을 제공하려 함
- 또한 정책을 변경하고 새 버전을 생성할 수 있기를 원함
👉 이 요구사항을 충족하는 작업 조합은? (2개 선택)
🔹 선택지 분석
- A. IAM 서비스 연결 역할(Service-linked role) 사용
→ 특정 AWS 서비스가 자동 생성하는 역할. 사용자 접근 제어와는 무관 ❌ - B. IAM 사용자 그룹에 사용자를 추가하고, 정책을 그룹에 연결
→ 효율적인 관리 방법. 그룹 단위로 정책 부여 가능 ✅ - C. AWS 관리형 정책 사용
→ 관리형 정책은 AWS가 제공, 버전 관리 불가 ❌ - D. 고객 관리형 정책(Customer managed policy) 사용
→ 직접 작성 및 관리 가능. 정책 버전 관리 가능 ✅ - E. 인라인 정책 사용
→ 사용자/그룹/역할에 직접 붙는 정책. 버전 관리 불가 ❌
✅ 정답: B, D
📝 쉬운 해설
- IAM 그룹 + 정책 연결
- 많은 사용자에게 정책을 쉽게 적용 가능
- 그룹 단위로 관리 → 운영 효율 ↑
- 고객 관리형 정책
- 직접 만든 정책 → 수정/새 버전 관리 가능
- AWS 관리형 정책/인라인 정책에는 없는 장점
📊 Mermaid 시각화
U[IAM 사용자] --> G[IAM 그룹]
G --> P[정책 연결]
P --> AWS[AWS 서비스 접근]
CM[고객 관리형 정책] -->|버전 관리 가능| P

🎯 암기 팁
👉 “IAM 다수 사용자 관리 = 그룹 + 고객 관리형 정책”
- 그룹: 사용자 묶어서 정책 적용
- 고객 관리형: 정책 버전 관리 가능
Q94.
A SysOps administrator wants to provide access to AWS services by attaching an IAM policy to multiple IAM users. The SysOps administrator also wants to be able to change the policy and create new versions.
Which combination of actions will meet these requirements? (Choose two)
A. Add the users to an IAM service-linked role. Attach the policy to the role.
B. Add the users to an IAM user group. Attach the policy to the group.
C. Create an AWS managed policy.
D. Create a customer managed policy.
E. Create an inline policy.
Answer: B, D
'AWS > AWS SOA-C02' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS SOA-C02] Multiple Choice-2 오답노트 14EA (0) | 2025.09.27 |
|---|---|
| [AWS SOA-C02] Multiple Choice-1 오답노트 15EA (0) | 2025.09.26 |
| [AWS SOA-C02] Q383 ~ Q429 오답노트 7EA (0) | 2025.09.26 |
| [AWS SOA-C02] Q301 ~ Q341 오답노트 5EA (0) | 2025.09.19 |
| Q101 ~ Q150 오답노트 21EA (0) | 2025.09.12 |