1. S3 Bucket 생성
 Amazon S3
Amazon S3
1-0. AWS Region : Asia Pacific (Seoul) ap-northeast-2
※ AWS Region 확인!
1-1. AWS Console에서 S3 Service 검색 → Create bucket 버튼 마우스로 클릭
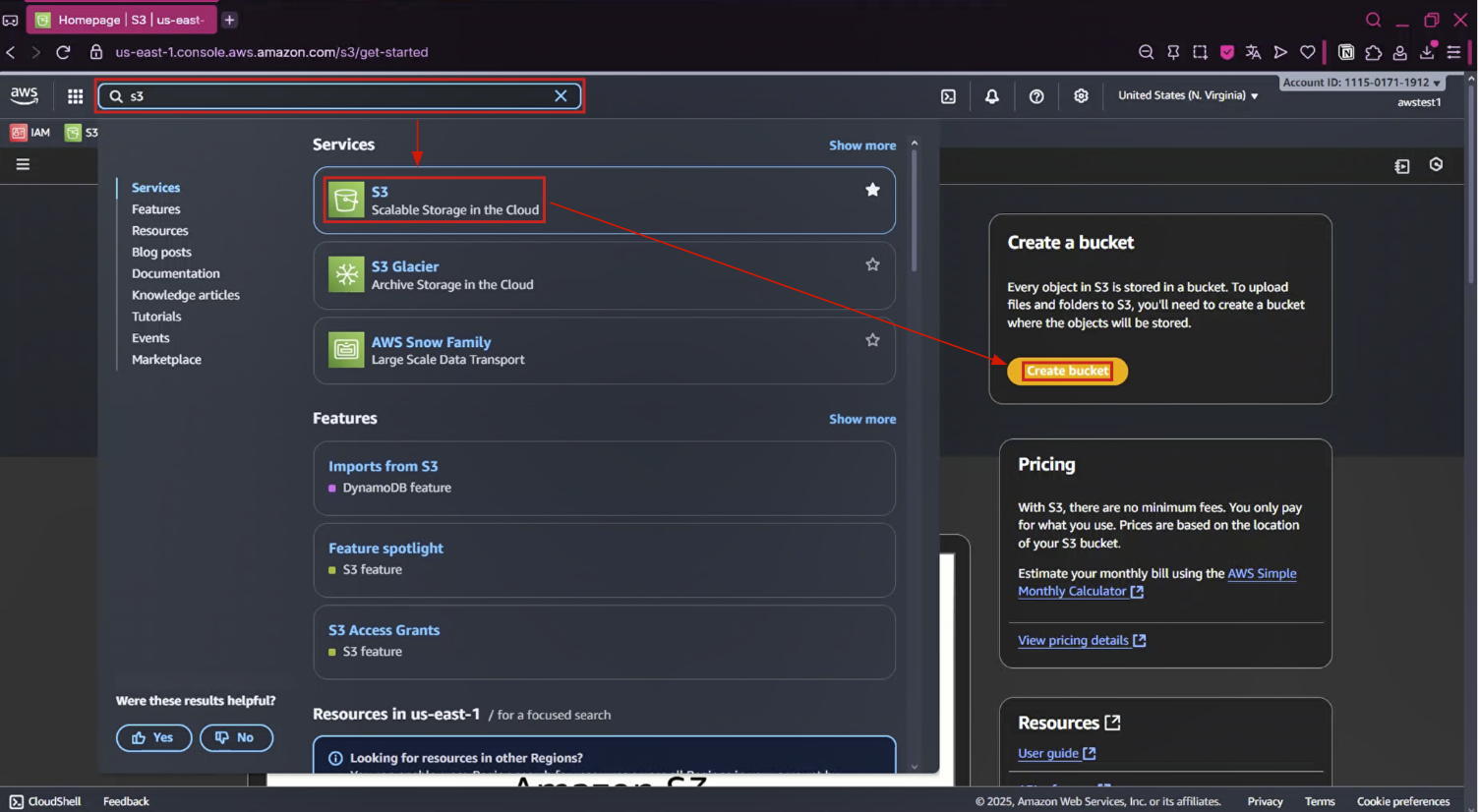

1-2. Bucket name 입력
Bucket name : my-shared-bucket-[이니셜]
Bucket name : my-shared-bucket-yjshin12345

1-3. Block Public Access Check Setting 그대로 유지
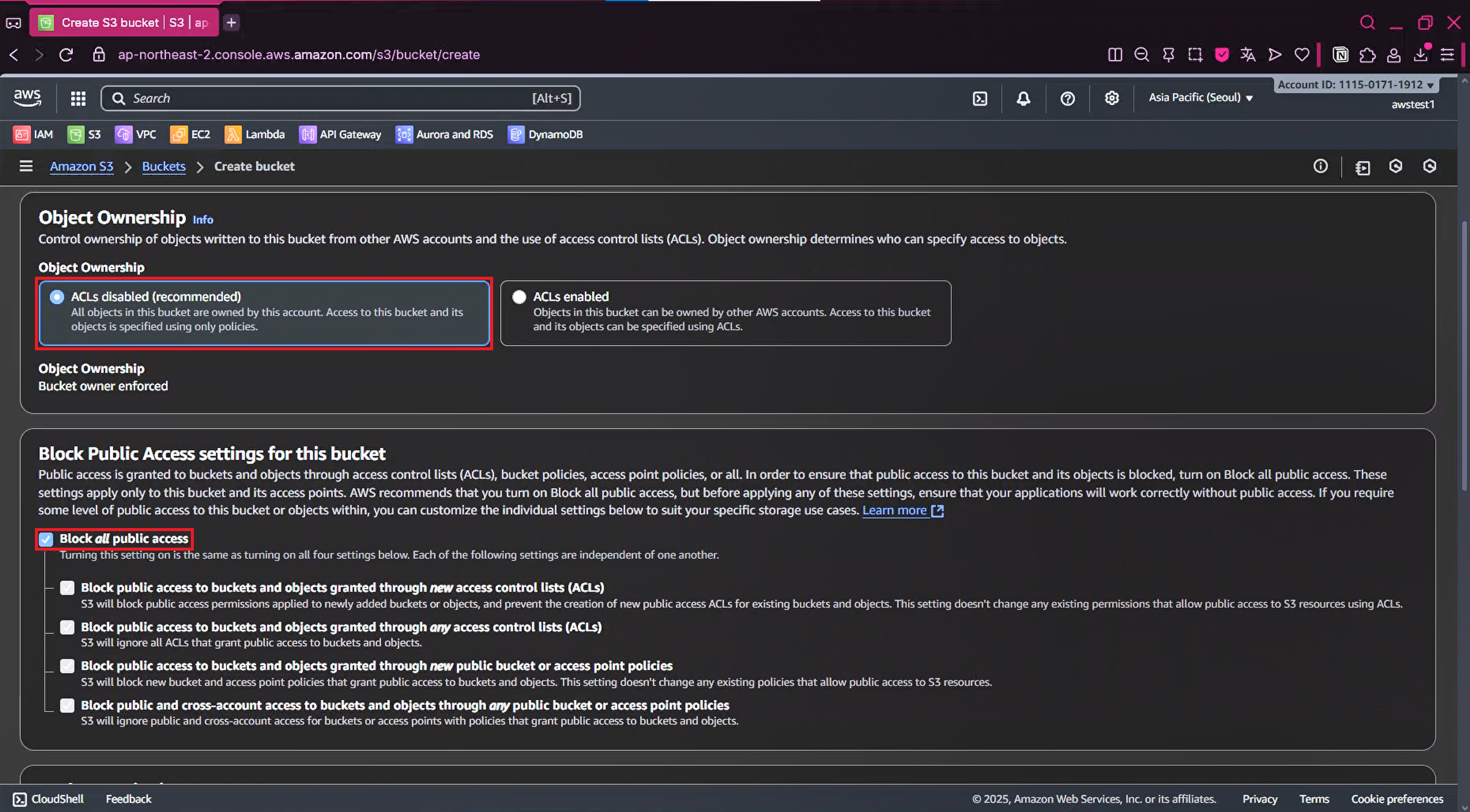
1-4. Versioning Default Setting 유지

1-5. Encryption Default Setting 유지 → Create bucket 버튼 마우스로 클릭

1-6. Amazon S3 Bucket 생성 완료

2. Access Point 생성
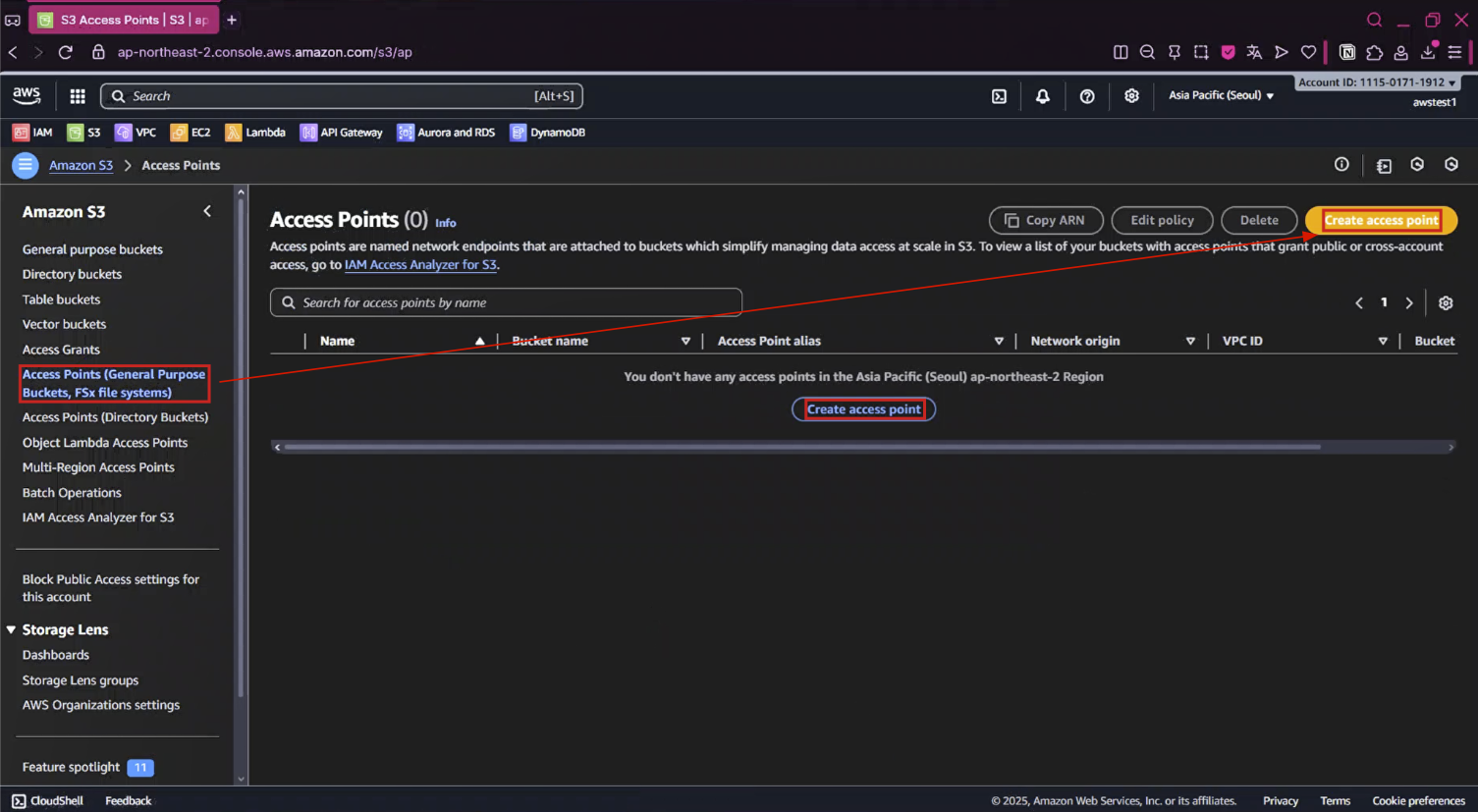
2-1. Amazon S3 왼쪽 메뉴에서 Access Points 마우스로 클릭 → Create access point 버튼 마우스로 클릭
- Access Points (General Purpose Buckets, FSx file systems) 마우스로 클릭
- Create access point 버튼 마우스로 클릭
2-2. Access point name 항목 입력 후 Bucket name - Browse S3 버튼 마우스로 클릭
Access point name: finance-ap

2-3. Choose a bucket to attach this access point to 팝업창 뜨면 위에서 생성한 버킷 이름 선택 → Choose bucket 버튼 마우스로 클릭

2-4. Block all public access Check 해제
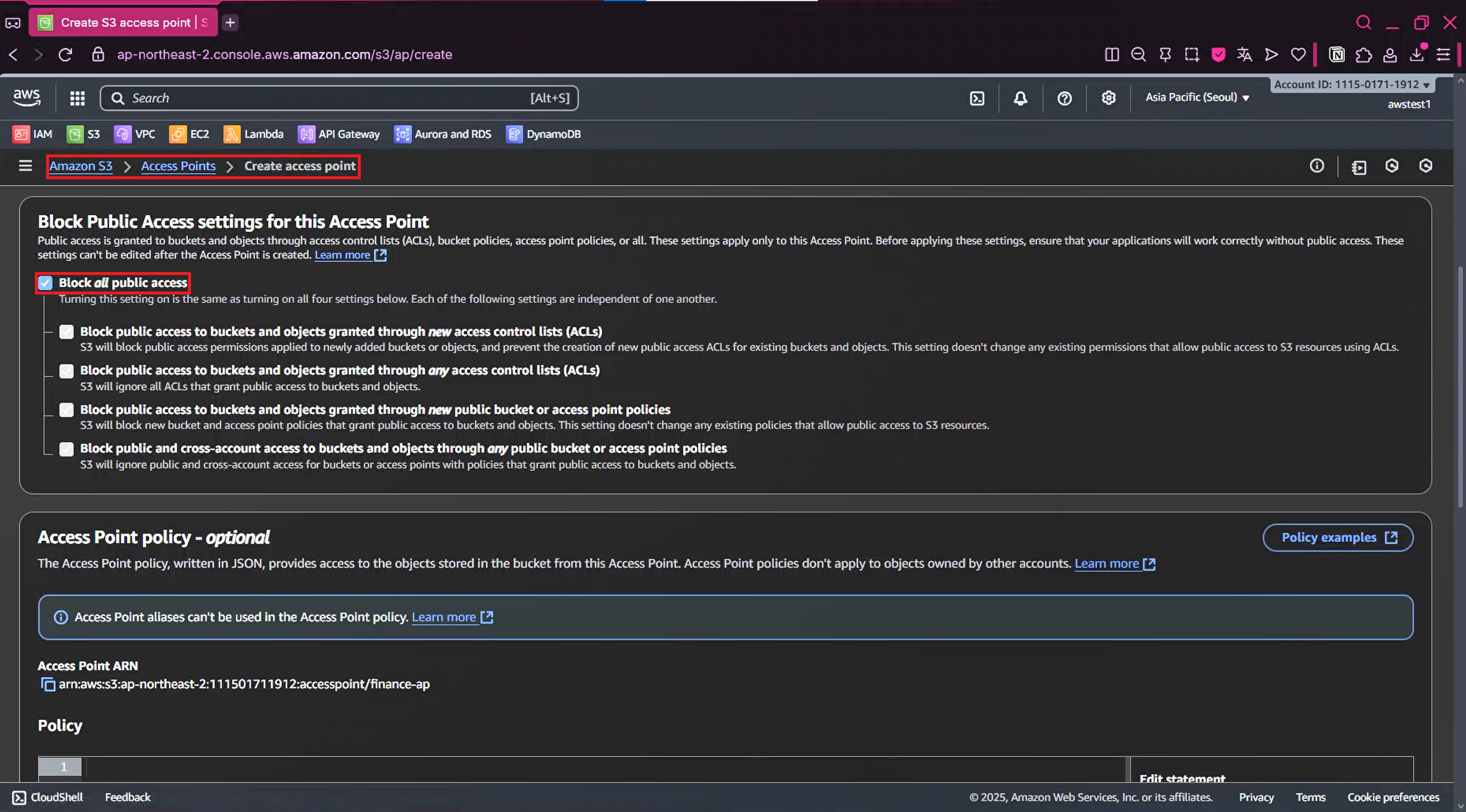

2-5. Access Point policy - 추후 설정 예정이므로 Default Setting 유지
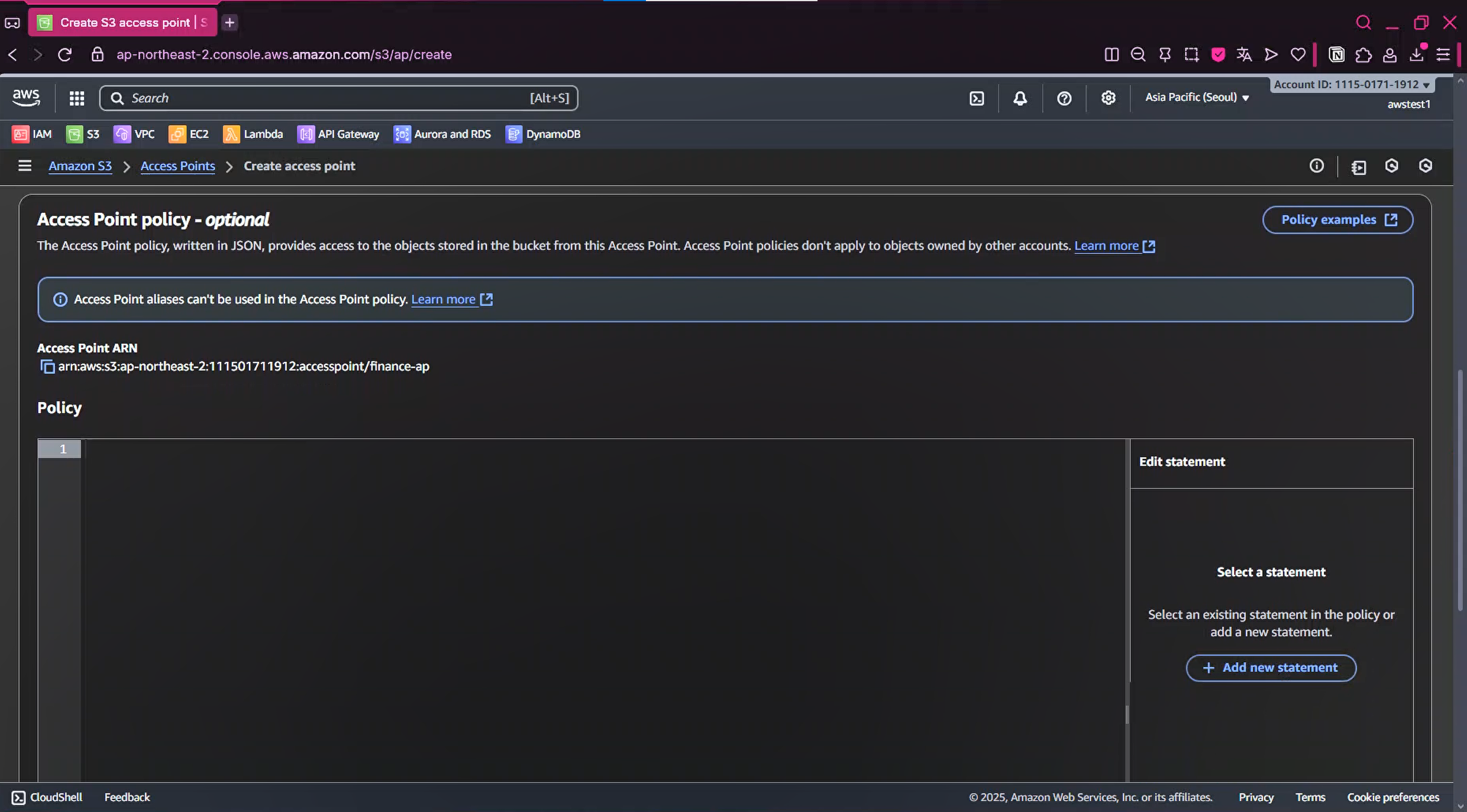
2-6. Create access point 버튼 마우스로 클릭
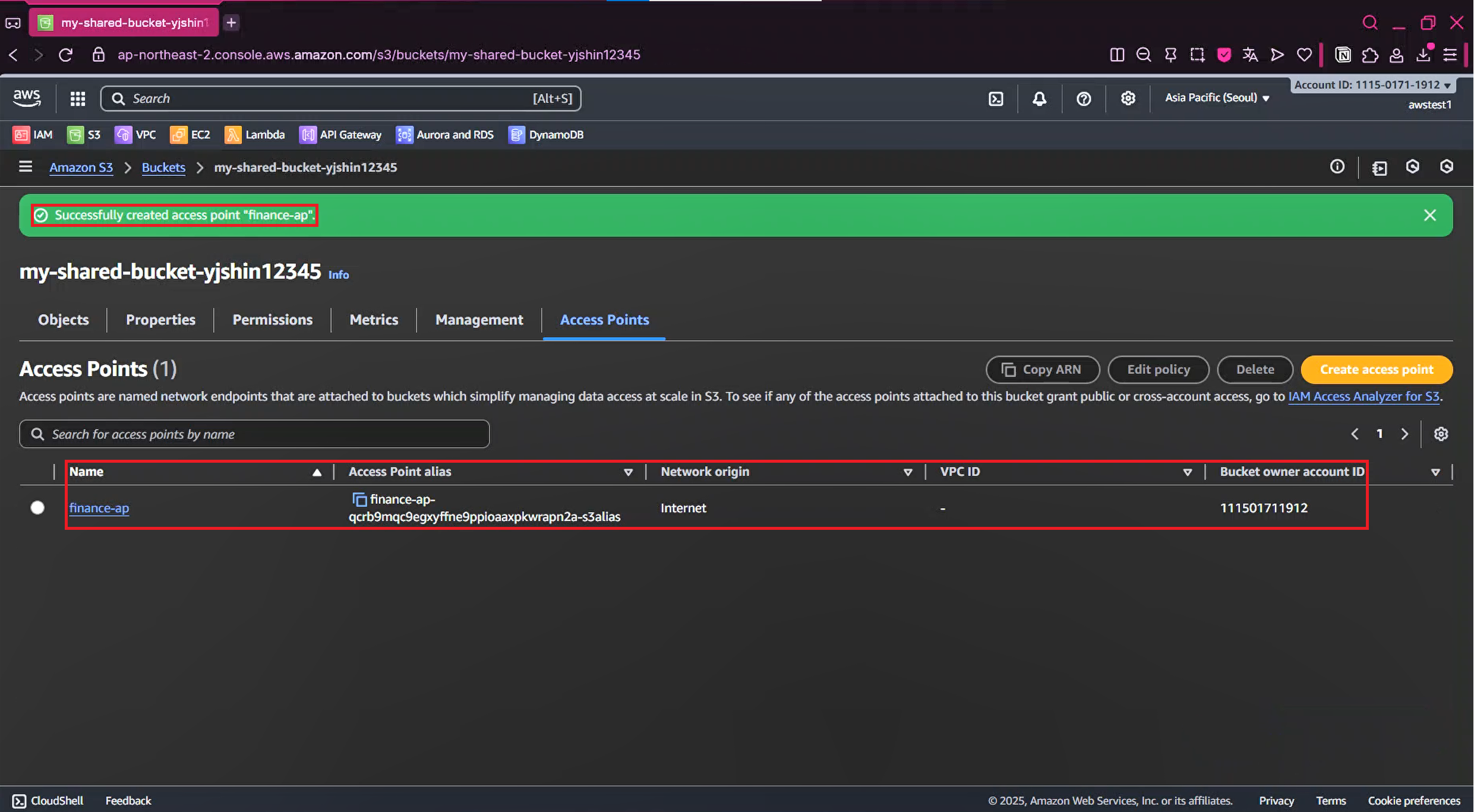
2-7. Amazon S3 Access Point 생성 완료
3. Access Point ARN 확인
3-1. Access Points 목록에서 finance-ap 마우스로 클릭 → Properties 탭 선택
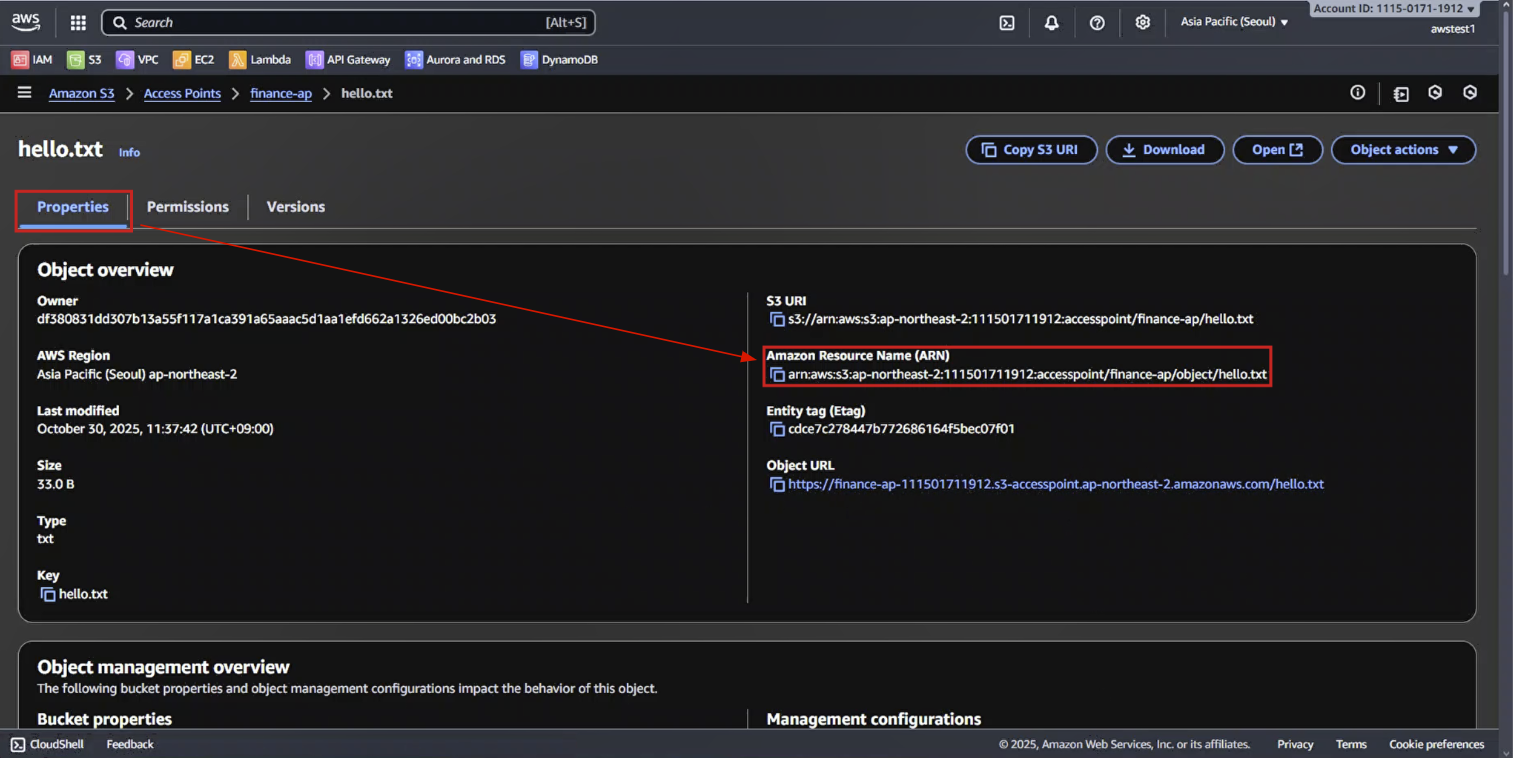
Amazon Resource Name (ARN) 확인 → 메모장에 복사해 놓기
arn:aws:s3:ap-northeast-2:123456789101:accesspoint/finance-ap
ARN은 정책 적용 및 접근 테스트 시 사용

S3 Bucket - Properties - ARN 복사 아님 XXX

4. Access Point 정책 설정
4-1. S3 - Access Points → finance-ap 선택 → Permissions 탭 선택 → Access point policy → [Edit] 버튼 마우스로 클릭

IAM 계정 ID - 12345678910
IAM 사용자 이름 - yjshin
Access Point ARN - 3-1.에서 복사한 Access Point ARN 주소 복붙
※ AWS 계정 하나로 실습하므로 IAM 계정 ID는 IAM User가 달라져도 동일
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowFinanceUser",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<계정ID>:user/<IAM사용자이름>"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"<Access Point ARN>/object/*"
]
}
]
}
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowFinanceUser",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::12345678910:user/yjshin"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:ap-northeast-2:12345678910:accesspoint/finance-ap/object/*"
}
]
}
4-2. Access point 정책 입력 완료 후 Save 버튼 마우스로 클릭


5. Access Point로 Object Upload Test
5-1. S3 Access Point - [Objects] 탭 선택 → [Upload] 버튼 마우스로 클릭
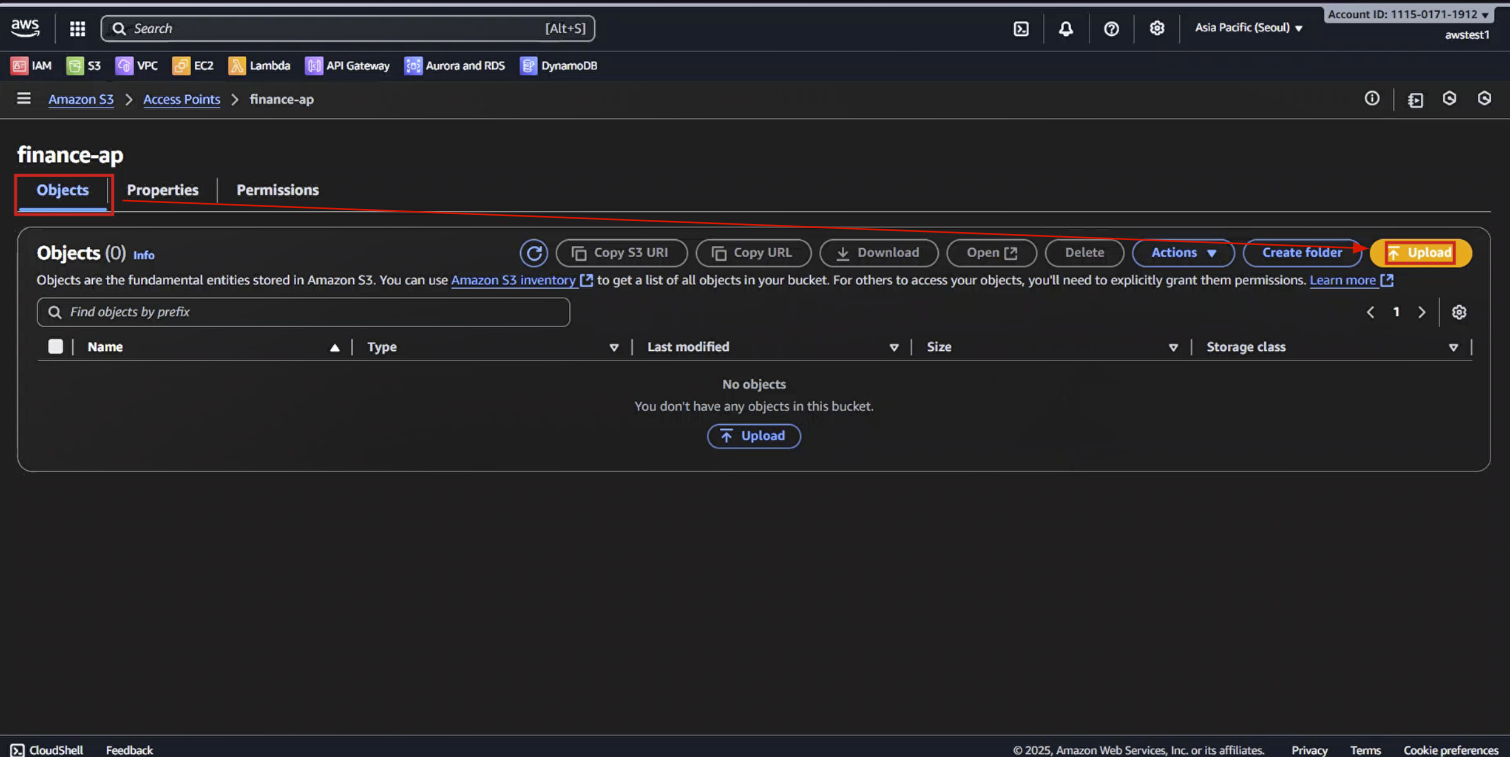
5-2. Upload - [Add files] → hello.txt file upload

5-3. hello.txt 파일 업로드 완료 후 [Upload] 버튼 마우스로 클릭

5-4. Upload 완료 메시지 확인 후 [Close] 버튼 마우스로 클릭

5-5. [Object] 탭 → hello.txt 파일 마우스로 클릭
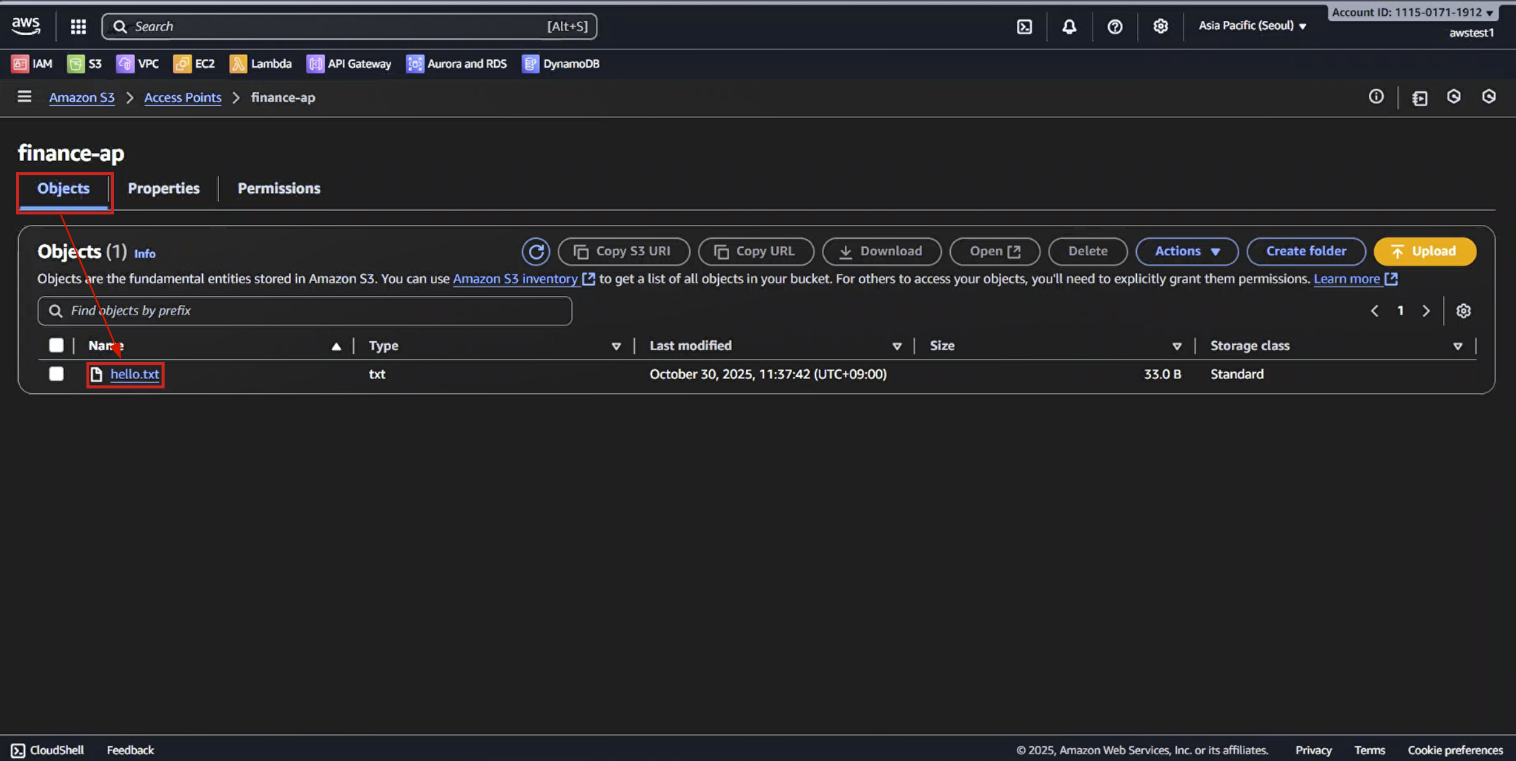
5-6. [Properties] - ARN 주소에 accesspoint 포함 확인
6. Access Point를 통한 접근 테스트
6-1. S3 Access Point 정책 설정한 IAM 사용자 로그인

6-2. Amazon S3 Console → Access Points (General Purpose Buckets, FSx file systems) → finance-ap 마우스로 클릭

6-3. [Objects] → hello.txt 파일 확인
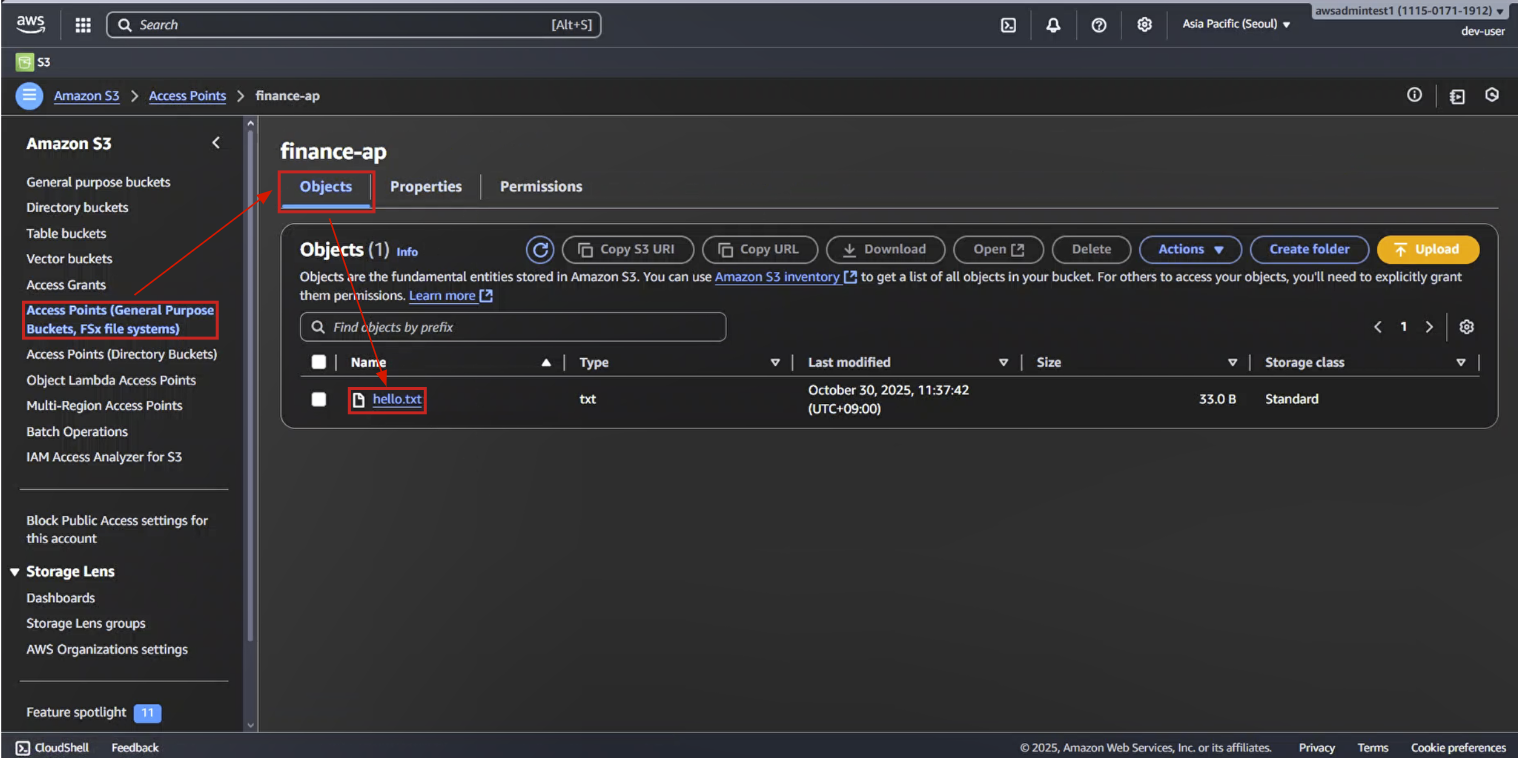
6-4. hello.txt 파일 접근 여부 확인
































